EUR Fundamental Analysis: ECB Rate Cut and Hawkish Tone Drive Euro Strength
The previous five-months and an outlook for the upcoming five weeks
Friday, 7 June 2024, Week 23: This report provides a fundamental analysis of the Euro (EUR), examining the key factors influencing its recent performance and potential future trajectory. The report covers fiscal policy, economic conditions, monetary policy, and geopolitical and market themes, providing insights for Forex traders.
Fiscal Policy
The Euro Area's fiscal policy is expected to tighten over the coming years, particularly in 2024. This tightening is primarily driven by the withdrawal of energy and inflation support measures implemented in response to the energy crisis and inflationary pressures. The European Commission's Spring 2024 Economic Forecast projects a decline in the euro area's aggregate deficit from 3.6% of GDP in 2023 to 2.8% in 2025. This fiscal consolidation is aimed at reducing government debt levels, which reached 88.6% of GDP at the end of 2023.
The tightening fiscal stance is likely to have a mixed impact on economic growth. On the one hand, it could weigh on demand in the short term as government spending is reduced. On the other hand, it could contribute to lower inflation and improve long-term sustainability, potentially supporting the Euro. The impact on economic indicators will depend on the specific measures implemented and their timing. For example, reductions in energy subsidies could lead to higher energy prices, while cuts to other spending could impact employment and consumer spending.
Economics
The Eurozone economy is showing signs of recovery after a period of stagnation. GDP growth rebounded to 0.3% in the first quarter of 2024, driven by net trade and household spending. However, the outlook remains uncertain, with the ECB's June 2024 staff projections highlighting risks to the downside over the medium term. These risks include a weaker global economy, geopolitical tensions, and the potential for stronger-than-expected effects from monetary policy tightening.
Economic Growth: The ECB projects economic growth to pick up to 0.9% in 2024, 1.4% in 2025, and 1.6% in 2026. This forecast is based on expectations of continued recovery in household spending, supported by rising wages and improved terms of trade. Stronger exports are also expected to contribute to growth, as global demand for goods and services rises. However, the negative impact of past monetary policy tightening is expected to weigh on growth, particularly in 2024.
Labour: The Eurozone labour market remains resilient, with the unemployment rate hitting a fresh record low of 6.4% in April 2024. Employment growth has been robust, with the number of employed persons rising by 0.3% in the first quarter of 2024. However, wage growth has slowed, with wages rising by 3.1% year-on-year in the fourth quarter of 2023, the least since the third quarter of 2022. The ECB's June 2024 staff projections suggest that wage growth will remain elevated but moderate over the projection horizon.
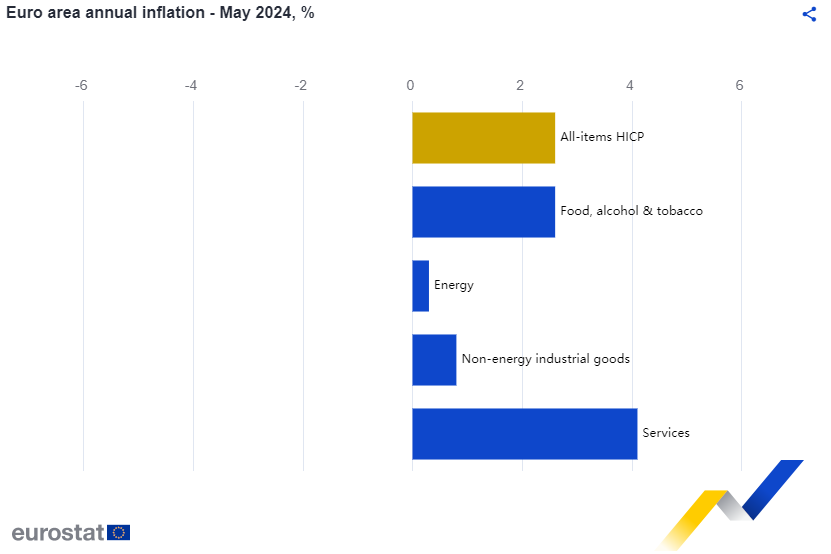
Price Changes: Inflation in the Euro Area rose for the first time in five months to 2.6% in May 2024, above forecasts of 2.5%. The core rate, which excludes prices for energy, food, alcohol, and tobacco, also increased to 2.9% from 2.7%. The ECB's June 2024 staff projections suggest that inflation will remain above the 2% target in the near term but decline towards the target over the second half of next year. This disinflationary path is expected to be driven by weaker growth in labour costs, the unfolding effects of restrictive monetary policy, and the fading impact of the energy crisis and the pandemic.
Trade: The Eurozone posted a trade surplus of €24.1 billion in March 2024, the largest since December 2020. This was driven by a sharp decline in imports, largely due to lower purchases of energy and other goods. Exports also fell, but at a slower pace. The current account surplus widened sharply to €44.5 billion in March 2024 from €27.0 billion a year earlier.
Monetary Policy
The ECB lowered its three key interest rates by 25 basis points in June 2024, marking a shift from nine months of stable rates. This decision was driven by the decline in inflation since September 2023. However, the ECB surprised markets with a hawkish tone, raising inflation forecasts and signalling a cautious approach to further cuts. The ECB's statement emphasised that it will keep policy rates sufficiently restrictive for as long as necessary to ensure that inflation returns to its 2% medium-term target in a timely manner.
The ECB's hawkish stance has contributed to Euro strength in recent weeks. The central bank's commitment to fighting inflation and its upward revision of inflation forecasts suggest that it is not in a hurry to cut rates further. This could continue to support the Euro, particularly if US economic data continues to soften, increasing the likelihood of Fed rate cuts.
Geopolitics and Market Themes
US Economic Slowdown and Fed Rate Cut Expectations: The US economy is showing signs of slowing, with recent data releases, such as the ADP employment report for May, coming in below expectations. This has fuelled speculation of multiple Fed rate cuts this year, weakening the USD and supporting the EUR.
Global Uncertainties and Safe-Haven Demand: Geopolitical tensions, including the ongoing war in Ukraine and the conflict in the Middle East, have contributed to periods of safe-haven demand for the yen and Swiss franc. However, as uncertainties ease, these currencies have weakened, indirectly supporting the EUR.
China's Economic Outlook: China's economic outlook remains uncertain, with concerns about the property sector and weak consumer spending. However, the manufacturing sector has been expanding, and China's export market share has remained above pre-pandemic levels. A potential slowdown in China's economy could weigh on global growth and impact the EUR.
Conclusion
The EUR is likely to remain supported in the near term, driven by the ECB's hawkish stance, the prospect of further softening in US economic data, and the potential for a tightening fiscal policy in the Euro Area. However, the upcoming US Non-Farm Payrolls report for May could introduce volatility. A strong report could challenge the narrative of a softening US labour market and reduce expectations of Fed rate cuts, potentially leading to a stronger USD and weaker EUR. Conversely, a weak report could solidify the dovish outlook for the Fed and further boost the EUR.
Overall, the EUR's fundamental outlook is mixed, with both supportive and bearish factors at play. Forex traders should closely monitor economic data releases, central bank communications, and geopolitical developments to assess the evolving balance of risks for the EUR.
References:
European Central Bank: https://www.ecb.europa.eu
EUROSTAT: https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat
Trading Economics: https://tradingeconomics.com