Euro Forex Reference JULY (updated)
DERBYSHIRE GB / JULY 31st, 2023 - Updated following CPI and GDP reports. Next update after the labour report on Tuesday the 1st of August, or before if any significant event occurs.
This is the Euro Forex Reference and contains factual information that has been researched from official sources as well as market commentators. It is intended to be used as a guide to aid in your analysis.
ABOUT
The euro is the currency of the European Union. It was introduced in 1999 and is now used by nineteen of the twenty-seven EU member states. The euro is the second-largest reserve currency in the world and is the most traded currency after the US dollar. It is a symbol of European unity and is seen as a sign of economic stability.
MONETARY POLICY
The European Central Bank
In the Euro Area, the benchmark interest rate is set by the Governing Council which consists of six members from the Executive Board plus governors of the national central banks from the nineteen countries using the euro.
July Meeting of the European Central Banks, Governing Council
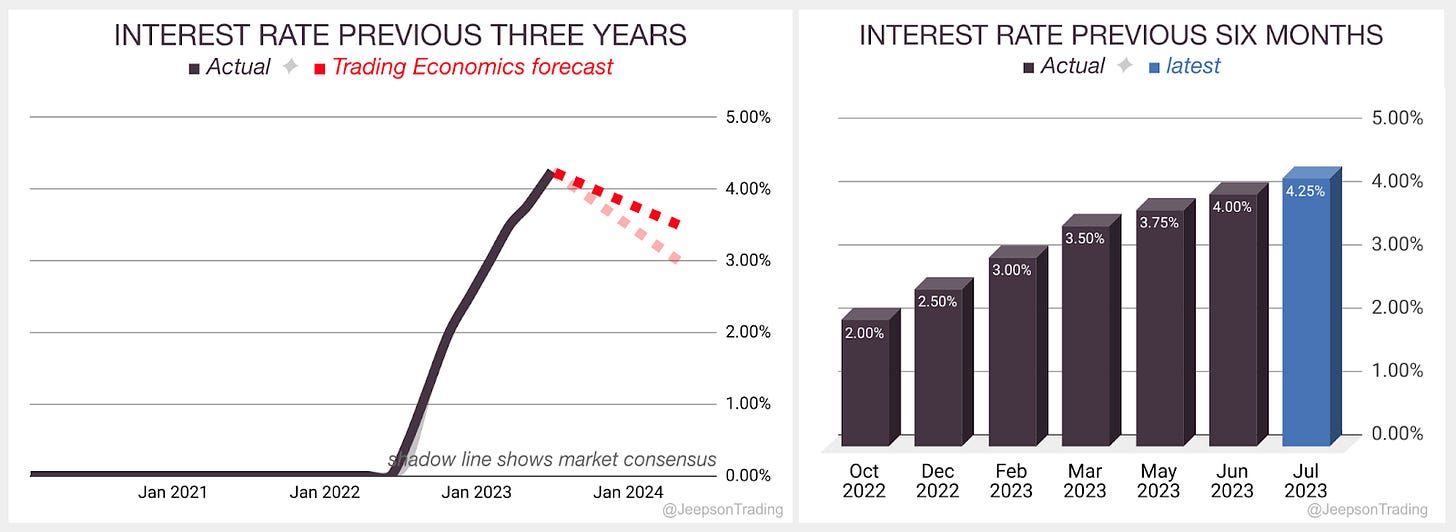
The Main Refinancing Operations rate was hiked by 0.25% in July to 4.25%, matching the 0.25% hike in May
This was as expected by analysts
This was the ninth consecutive rate hike since this cycle began last year in July 2022
Over the previous three years, since the start of 2020, the interest rate in the Euro Area (EA) has increased from 0.00% to 4.25%. Over the previous six months, the rate has continued to climb. Trading Economics expects the interest rate to be hiked again to a peak of 2.50% in Q3 ‘23
The next meeting is on Thursday the 14th of September
The Governing Councils June statement summarised:
Rates raised by 25 basis points to combat high inflation
Inflation is still high and expected to remain high for an extended period
The past rate increases are having a dampening effect on demand, which is helping to bring inflation back to target
Rates will be kept high until inflation returns to target
Rates will be adjusted based on incoming data and the strength of monetary policy transmission
The ECB will no longer pay interest on minimum reserves, which will preserve the effectiveness of monetary policy and improve efficiency
The APP portfolio is shrinking slowly and predictably. The PEPP portfolio will be reinvested until 2024. The Governing Council will be flexible in reinvesting PEPP redemptions.
The ECB will monitor how TLTROs and their repayments affect monetary policy.
Sources: European Central Bank, Macroeconomic Projections, Trading Economics, FXStreet
Macroeconomic Projections
The Governing Council revised its macroeconomic projections at their June meeting. They will update them again in September.
Economic activity is expected to slow in 2023, but to rebound in 2024 and 2025.
Inflation is expected to remain high in 2023, but to decline in 2024 and 2025.
The main drivers of economic growth are expected to be:
strong labour market, unemployment hitting new historical lows
rebound in foreign demand
resolution of supply chain bottlenecks
The main drivers of inflation are expected to be:
higher energy prices
tighter labour markets
higher unit labour costs
ECONOMIC DATA
Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
In the US, GDP Growth Rate measures the yearly change in the price of goods and services purchased by consumers.
GDP Growth Rate Flash Estimate for Q2 2023
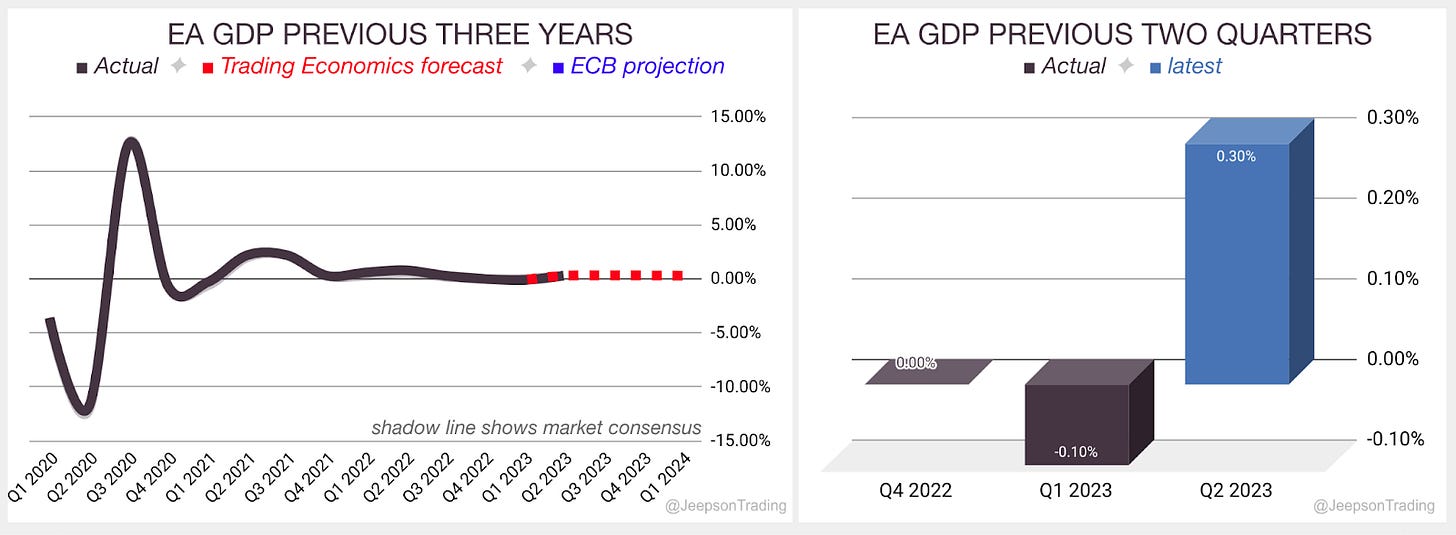
GDP in the EA for Q2 strengthened to 0.3% from - 0.1% quarterly contraction in Q1 2022
Slightly higher than the 0.20% expansion expected by analysts
Ireland (+3.3%) saw the highest Q2 2023 GDP growth, followed by Lithuania (+2.8%). Sweden (-1.5%), Latvia (-0.6%), Austria (-0.4%) and Italy (-0.3%) saw declines. Ireland (+2.8%), Portugal (+2.3%) and Spain (+1.8%) saw the highest year-over-year growth, while Sweden (-2.4%), Czechia (-0.6%) and Latvia (-0.5%) saw declines
Over the previous three years, since the start of 2020, the GDP growth rate in the Euro Area (EA)has been climbing from a low of -4.3% to a high of 14.6% . Over the previous six months, the rate has been falling although recently reversed. Trading Economics expects a rise to 0.4% in Q3 ‘23 while the Governing Council have forecasted ‘23 0.9% which is revised down from 1.0% although this is for Real GDP
The second estimate Q2 report is due on Wednesday the 16th of August
Sources: Eurostat, Trading Economics, FXStreet
CONSUMER PRICE INDEX
Measures the yearly change in the price of goods and services purchased by consumers using the weighted average of the Harmonised Index of Consumer Price (HICP) aggregates.
Flash CPI for July
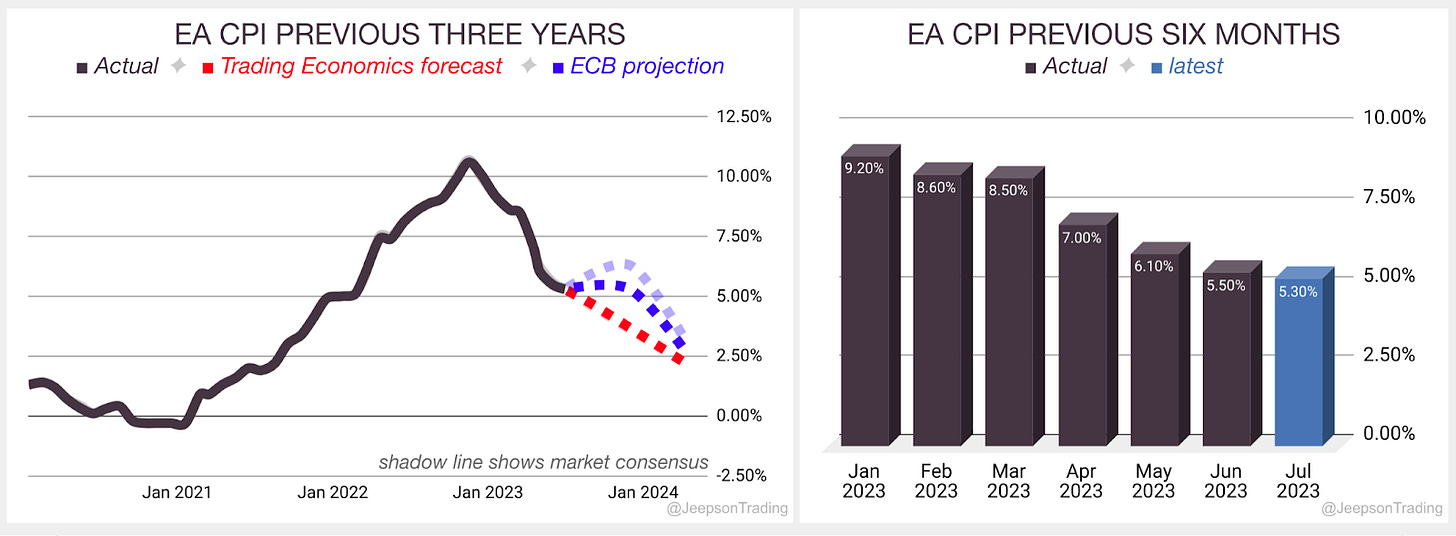
CPI in the EA for July slowed to 5.3% annual inflation from 5.5% in June
This was as expected by analysts
Slowing rate was not helped by a climb in food inflation
Over the previous three years, since the start of 2020, the CPI rate in the Euro Area (EA)has been climbing quickly from a low of -0.3% to a high of 10.6% . Over the previous six months, the rate has been falling. Trading Economics expects a fall to 4.7% in Q3 ‘23 while the Governing Council have forecasted ‘23 at 5.4% which is revised up from 5.3% although this is for HICP
The final July report is due on Friday the 18th of August
Sources: Eurostat, Trading Economics, FXStreet
LABOUR
Measures the number of people actively looking for a job as a percentage of the labour force.
Labour Report for May
Unemployment in the EA for May remained at 6.5%, the same level as April
This was as expected by analysts
Trading Economics have retained their Q2 2023 unemployment rate forecast at 6.6%
Over the previous three years, unemployment has fallen from a high of 8.3% in Mar ‘21 to a low 6.5% in May ‘22. This fall has stabilised in the past six months.
Over the previous three years, since the start of 2020, the unemployment rate in the Euro Area (EA)has been falling from a high of 8.3% to a low of 6.5% . Over the previous six months, the rate has since stabilised. Trading Economics expects it to remain steady at 6.6% in Q3 ‘23
The June report is due on Tuesday the 1st of August
Sources: Eurostat, Trading Economics, FXStreet
MARKET NARRATIVES
Russia–EU gas dispute
The Russia-EU gas dispute has caused an increase in the cost of energy which has reduced the spending power of consumers and resulted in slower economic growth. This is likely to lead to reduced foreign investment in the stock market and is expected to apply downward pressure on the Euro’s value.
The EU imported 83% of its natural gas in 2021, with 50% of that coming from Russia. However, after Russia invaded Ukraine in March 2022, the EU needed to diversify its gas imports and seek out more reliable suppliers.
The global energy market is likely to become more volatile in the years to come, due to a number of factors, including the increasing demand for energy from developing countries, the growing importance of renewable energy, and the uncertainty surrounding the future of fossil fuels. Europe is debating how to separate gas prices from electricity prices so that consumers are more protected from the volatile price of gas, which has been a major driver of rising electricity prices.
2022: In the wake of Russia's invasion of Ukraine, Russia began demanding that its natural gas customers pay in rubles, rather than euros or dollars. This led to a number of European countries, including Poland, Bulgaria, and Finland, refusing to pay, and subsequently having their gas supplies cut off. Russia also cut off gas supplies to Ukraine, which was a major transit point for Russian gas to Europe. These events have had a significant impact on the European energy market, causing gas prices to skyrocket and raising concerns about energy security.
GEOPOLITICAL EVENTS
Russian Invasion of Ukraine
The war is having a detrimental effect on the global and EA economy by causing higher energy prices, supply chain disruptions, financial market volatility, refugee crisis and geopolitical uncertainty.
2021: 92,000 Russian troops are amassed at the Ukraine border and President Putin proposes a prohibition of Ukraine joining NATO which is rejected.
2022: On the 21st of February, President Putin ordered Russian forces to enter the separatist republics in eastern Ukraine and announced recognition of the two pro-Russian breakaway regions (Donetsk People's Republic and Luhansk People's Republic). NATO applied sanctions and scaled them up as the war progressed. Ukraine mounted a counter-offensive which regained lost territory and as winter arrived, a stalemate began.
2023: Russian began a new offensive in January although gained little ground. In early June, Ukraine began its counteroffensive although progress has been slow even as Russia faced mutiny from the short-lived Wagner rebellion.
Gavin Pearson
Retail trader since 2008
Specialises in forex G7 currencies
Funded account from the5ers.com
Member of the eToro Popular Investors Program
Regular contributor to FXStreet.com analysis and education pages
Jeepson Trading Fund
Returned 27% in 2022 and 5.8% in 2023 H1
Forex focused
Copy Trading available at eToro
eToro
eToro is a social trading platform
Users can copy trades by clicking the "Copy" button on the profile page
Disclaimer
Past performance is not indicative of future results
Trading involves risk, and you could lose money
-end-