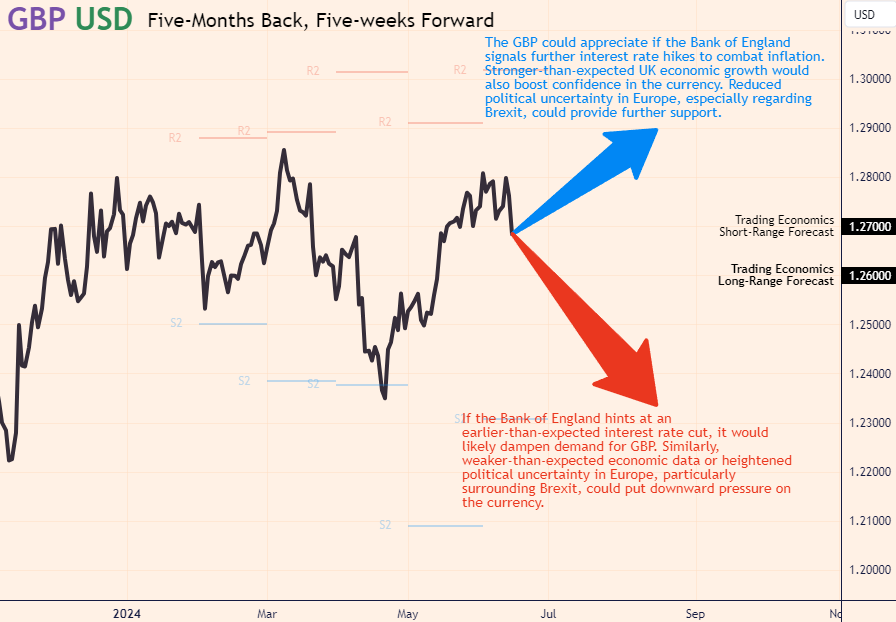
GBP Fundamental Analysis: Sterling Rebounds Over Five Months, Stumbles Over Five Weeks, BoE Decision (20th June) Will Be Pivotal
Saturday, 15 June 2024, Week 24: The British pound has experienced a notable rebound over the past five months, recovering from lows against the US dollar and other major currencies. However, recent weeks have seen sterling lose some ground as political uncertainty in Europe and concerns about the UK's economic outlook weigh on investor sentiment. The upcoming Bank of England (BoE) monetary policy announcement on 20th June will be pivotal in determining the pound's next direction. This report will delve into the key market fundamentals affecting the UK economy, monetary policy, and the GBP, providing insights for Forex traders.
Fiscal Policy
The UK government's fiscal policy has been expansionary in recent years, with significant spending to support the economy during the pandemic and the energy crisis. However, the fiscal position remains challenging, with high levels of debt and a subdued economic outlook. The Spring Budget 2024 announced a package of net tax cuts, including a further 2p cut to the main rates of employee and self-employed national insurance contributions. This is expected to provide a boost to household incomes and consumption in the near term. However, the cost of these tax cuts is partially recouped by tax rises in later years, including reform of the non-domicile regime.
Over the next five weeks, the focus will be on the implementation of the Budget measures and their impact on the economy. The government's ability to meet its fiscal targets, including reducing debt as a share of GDP, will be closely watched by markets. Any signs of fiscal slippage or a deterioration in the economic outlook could weigh on the pound.
Economics
Economic Growth
The UK economy has been struggling in recent quarters, with GDP growth slowing sharply and even contracting in the second half of 2023. The latest data show that GDP grew by just 0.1% in 2023, well below the pre-pandemic trend. The weakness in growth has been driven by a number of factors, including high inflation, rising interest rates, and the ongoing impact of Brexit.
The outlook for growth remains subdued, with the BoE forecasting GDP growth of 0.8% in 2024 and 1.9% in 2025. The economy is expected to operate with a margin of slack, which should help to ease inflationary pressures. However, there are downside risks to the growth outlook, including the possibility of a sharper slowdown in global growth, further increases in energy prices, and a more pronounced impact of Brexit on trade.
Labour
The UK labour market remains tight, with the unemployment rate at a historically low level of 3.8%. However, there are signs that the labour market is beginning to cool, with vacancy growth slowing and employment growth moderating. The latest data show that the number of payrolled employees decreased by 36,000 in April 2024.
The outlook for the labour market is uncertain, with the BoE forecasting a modest rise in the unemployment rate to 4.5% by the end of 2024. The tightness in the labour market is expected to ease as economic growth slows. However, there are upside risks to the unemployment forecast, including the possibility of a sharper slowdown in demand or a more pronounced impact of Brexit on migration.
Price Changes
CPI inflation has fallen sharply from its peak of 11.1% in October 2022, reaching 3.2% in March 2024. The decline in inflation has been driven by a number of factors, including falling energy prices, easing supply chain bottlenecks, and the impact of higher interest rates.
The outlook for inflation is for it to fall further in the near term, with the BoE forecasting CPI inflation of 2.2% in 2024 and 1.5% in 2025. However, there are upside risks to the inflation outlook, including the possibility of a resurgence in global energy prices, a more persistent increase in core inflation, and a weaker pound.
Trade
The UK's trade deficit widened to a near two-year high of £6.75 billion in April 2024. Imports rose by 7.2% to a near one-year high of £76.9 billion, while exports fell by 0.7% to £70.1 billion.
The outlook for trade is for the deficit to remain elevated, with the BoE forecasting export and import volumes to grow by an average of 0.3% and 0.1% a year, respectively, from 2024 to 2028. The weakness in trade is being driven by a number of factors, including sluggish global growth, the ongoing impact of Brexit, and the recent appreciation of the pound.
Monetary Policy
The BoE has raised interest rates aggressively over the past year, with Bank Rate rising from 0.1% in December 2021 to 5.25% in May 2024. The BoE has been seeking to bring inflation back to its 2% target. The latest Monetary Policy Report, published in May 2024, states that "Monetary policy will need to remain restrictive for sufficiently long to return inflation to the 2% target sustainably in the medium term in line with the MPC’s remit."
The outlook for monetary policy is for Bank Rate to remain at its current level for some time, with the BoE forecasting only one rate cut this year. The BoE will be closely monitoring economic data, particularly inflation and wage growth, to determine the appropriate path for interest rates.
Over the next five weeks, the key event for monetary policy will be the BoE's announcement on 20th June. The market is currently pricing in a 50% chance of a rate cut at this meeting. Any signs that the BoE is becoming more hawkish, for example by signalling that it is prepared to raise rates further, could support the pound. Conversely, any signs that the BoE is becoming more dovish, for example by signalling that it is prepared to cut rates sooner than expected, could weigh on the pound.
Geopolitics and Market Themes
Several geopolitical situations and market themes are currently influencing or could influence the UK economy, monetary policy, and the GBP. These include:
Geopolitical Tensions
Synopsis: Geopolitical tensions, including the ongoing war in Ukraine and rising tensions between the US and China, are contributing to market volatility and risk aversion. These tensions are impacting commodity prices, supply chains, and investor sentiment.
Key Developments:
Russia continues its military offensive in Ukraine, raising concerns about energy security and global economic growth.
The US and China are engaged in a strategic competition, leading to trade disputes and technological decoupling.
Market Impact:
Oil prices remain elevated due to concerns about supply disruptions related to the war in Ukraine.
Gold prices are finding support as a safe-haven asset amid geopolitical uncertainty.
Global supply chains are facing disruptions, contributing to inflationary pressures.
Political Uncertainty in Europe
Synopsis: Political instability in France following the European Parliament elections is raising concerns about fiscal stability and the country's ability to implement reforms. The prospect of a far-right victory in the upcoming parliamentary elections is adding to market uncertainty.
Key Developments:
French President Macron called for snap legislative elections after the far-right National Rally's strong performance in the EU elections.
The gap between French and German bond yields has widened, reflecting concerns about France's fiscal outlook.
European equities have declined as investors assess the potential for political instability in France.
Market Impact:
The euro has weakened against the dollar, reflecting concerns about political and fiscal risks in France.
French bond yields have risen, while German bund yields have fallen as investors seek safe-haven assets.
European equities are facing headwinds from political uncertainty, particularly in the financial sector.
Global Inflation and Monetary Policy Divergence
Synopsis: Inflation remains a concern globally, prompting central banks to maintain a hawkish stance. However, recent data suggests that inflation may be easing in some major economies, leading to speculation about the timing and extent of future rate cuts. The divergence in monetary policy between the US Federal Reserve and other central banks, such as the Bank of Japan, is creating volatility in currency markets.
Key Developments:
The US Federal Reserve held interest rates steady but signalled a more cautious approach to rate cuts, projecting only one reduction this year.
The European Central Bank cut interest rates by 25bps, marking a shift from its previous stance of holding rates steady.
The Bank of Japan maintained its ultra-loose monetary policy, defying market expectations for a move towards tightening.
Market Impact:
The US dollar has strengthened against most major currencies, as the Fed's hawkish stance contrasts with easing policies in other regions.
US Treasury yields have fallen as investors anticipate potential rate cuts later this year.
The Japanese yen has weakened to multi-decade lows against the dollar, reflecting the divergence in monetary policy between the Fed and the BOJ.
Conclusion
The outlook for the GBP over the next five weeks is uncertain, with a number of factors likely to influence its direction. The upcoming BoE monetary policy announcement on 20th June will be a key event to watch.
Upward Support
The GBP could come under upward support if:
The BoE signals that it is prepared to raise interest rates further to combat inflation.
The UK economy shows signs of stronger-than-expected growth.
Political uncertainty in Europe eases.
Indifference
The GBP could trade sideways if:
The BoE maintains its current policy stance, with no clear signals about the future path of interest rates.
The UK economy continues to grow at a modest pace, with no clear signs of either acceleration or deceleration.
Political uncertainty in Europe persists.
Downside Pressure
The GBP could come under downside pressure if:
The BoE signals that it is prepared to cut interest rates sooner than expected.
The UK economy shows signs of weaker-than-expected growth.
Political uncertainty in Europe intensifies.
The BoE's monetary policy announcement on 20th June will be pivotal in determining the pound's next direction. If the BoE signals that it is prepared to raise rates further, this could provide a significant boost to the pound. Conversely, if the BoE signals that it is prepared to cut rates sooner than expected, this could weigh heavily on the pound.
References
Bank of England: https://www.bankofengland.co.uk/
Office for National Statistics: https://www.ons.gov.uk/
HM Treasury: https://www.gov.uk/government/organisations/hm-treasury
Trading Economics: https://tradingeconomics.com/
Bloomberg: https://www.bloomberg.com/
Reuters: https://www.reuters.com/
Financial Times: https://www.ft.com/
Office for Budget Responsibility