Pound Sterling Forex Reference May (CPI Update)
DERBYSHIRE GB / MAY 27 - This is the Pound Sterling Forex Reference and contains factual information that has been researched from official sources as well as market commentators. It is intended to be used as a guide to aid in your analysis.
ABOUT THE POUND STERLING
The pound sterling, or GBP, is the official currency of the United Kingdom. It is the oldest currency in continuous use and is the fourth most traded currency in the world.
MONETARY POLICY
The Bank of England
The Bank of England is the Central Bank of the United Kingdom and monetary policy decisions are made by the nine members of the Monetary Policy Committee (MPC).
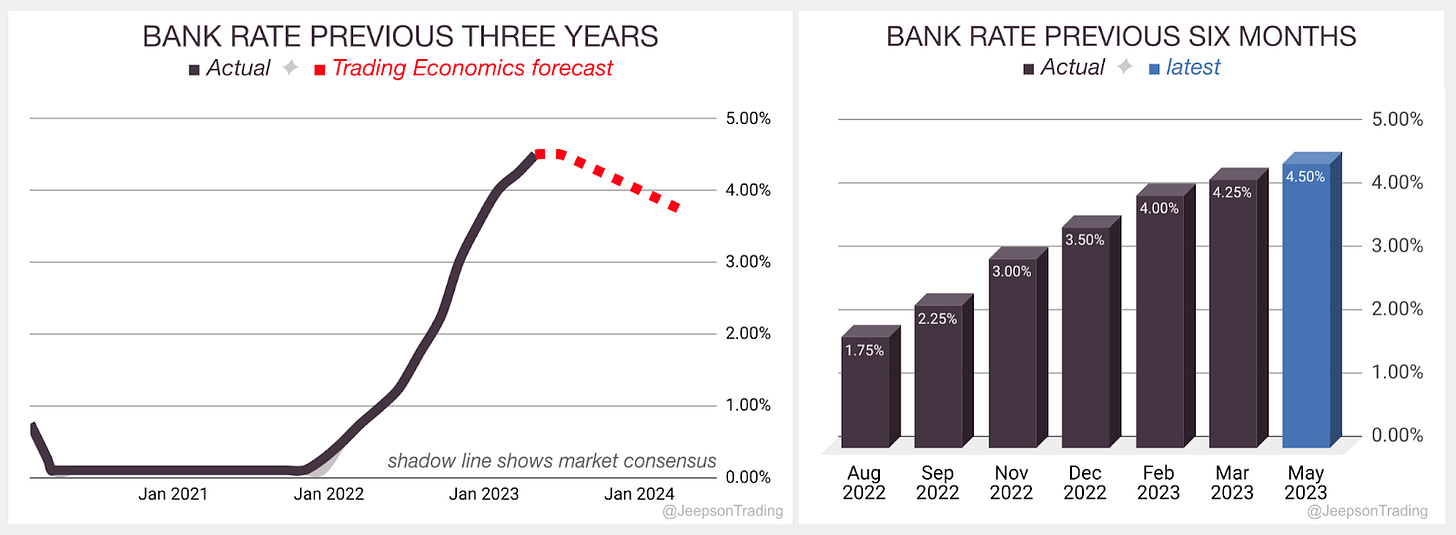
The Bank of England's Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) voted to increase the Bank Rate by 0.25 percentage points to 4.50% on the 11th of March. This is the eleventh consecutive rate hike in an effort to bring inflation back to its 2% target. The MPC expects CPI inflation to fall sharply from April but will continue to raise interest rates if necessary to return inflation to the 2% target.
The next Monetary Policy Committee meeting is on Thursday, June 22.
The Monetary Policy Committee‘s May statement contained cautious sentiments with regards to the approach to monetary policy:
The Committee judges that the risks around the inflation forecast are skewed significantly to the upside
The Committee will continue to closely monitor indications of persistent inflationary pressures
The Committee will adjust Bank Rate as necessary to return inflation to the 2% target sustainably in the medium term.
Sources: The Bank of England, Trading Economics
May 2023 Monetary Policy Report
The Bank of England's Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) revised its economic forecast for the UK at their May meeting. They will update them again in August.
Increased the Bank Rate by 0.25 percentage points, to 4.5%
Expects CPI inflation to fall sharply from April, but to remain above the 2% target in the medium term
Continuing to address the risk of more persistent strength in domestic price and wage setting
Continuing to closely monitor indications of persistent inflationary pressures
Will adjust Bank Rate as necessary to return inflation to the 2% target sustainably in the medium term
Inflation has been rising sharply in recent months, driven by
the war in Ukraine
rising energy prices
supply chain disruptions
The MPC is concerned that inflation could become entrenched if it is not brought under control
The raising of the Bank Rate is to slow the pace of economic growth and bring inflation back down to the 2% target
ECONOMIC DATA
Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
Measures the quarter on quarter change of the inflation-adjusted value of produced goods and services.
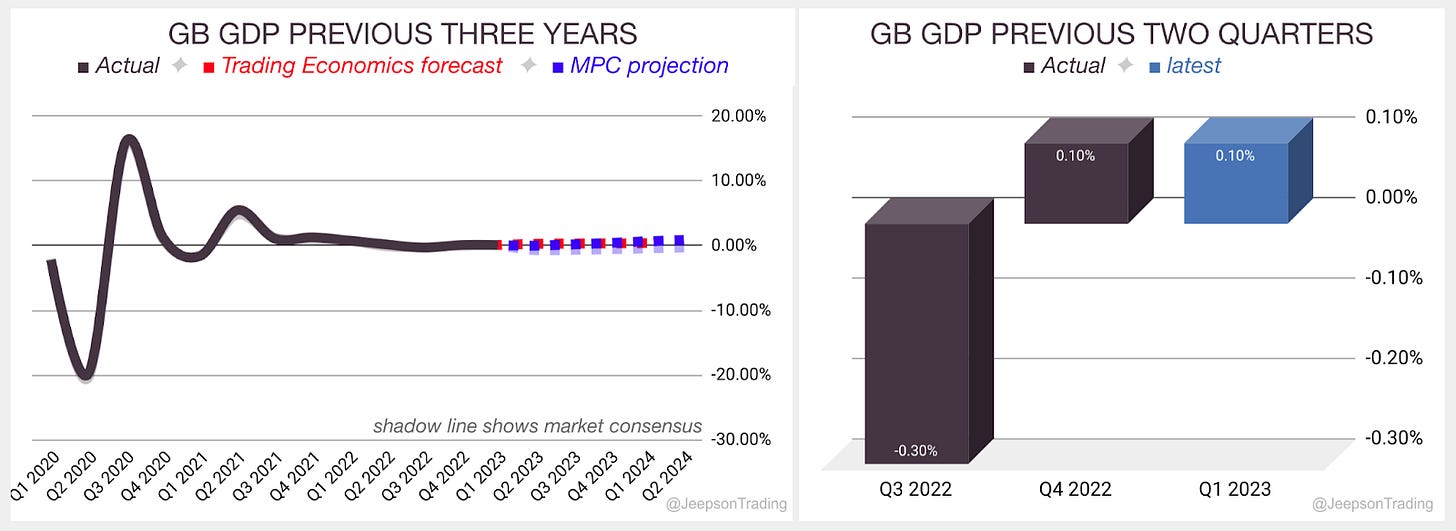
UK GDP grew by 0.1% in Q1 2023, matching expectations. Services and Production grew 0.1% and construction grew 0.7%. Real GDP is 0.5% below pre-COVID levels. In expenditure terms, household consumption showed no growth on the quarter, while there was a positive contribution from gross fixed capital formation.
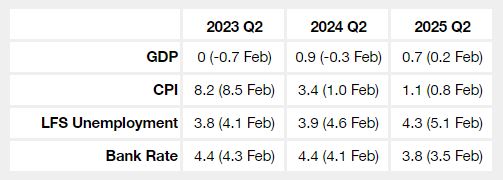
The MPC projects growth to expand by 0.9% in 2024, up from -0.3% previously. Trading Economics forecasts Q2 growth of 0.3%, up from 0.2% previously. The Q1 2023 final report is due on Friday the 30th of June.
The outlook for growth remains uncertain, but it can be characterised as optimistic improvement. This means that expansion is likely and at higher levels than previously thought.
Sources: Office for National Statistics, Trading Economics
CONSUMER PRICE INDEX
Measures the yearly change in the price of goods and services purchased by consumers.
Headline CPI in the UK fell to 8.7% inflation in April, much higher than the 8.2% expected but far below the previous 10.1%. The significant moving category was ‘Housing & Utilities’ which fell from 26.1% to 12.3%.
The MPC has a projection of 8.2% for Q2 with a fall to 3.4% in Q2 2024. Trading Economics are forecasting 8.0% in Q2. The April report is due on Wednesday the 21st of June.
The outlook for CPI can be characterised as a pessimistic improvement. This means that a lower rate of inflation is likely, but it is not expected to be as low as projected.
Sources: Office for National Statistics, Trading Economics
LABOUR
Unemployment rate measures the number of people actively looking for a job as a percentage of the labour force.
Employment increased slightly to 75.9% from 75.8%, driven by part-time and self-employed
Payrolled employees decreased by 136,000
Unemployment rate increased slightly to 3.9% from 3.8%
Inactivity rate decreased to 21.0%
Vacancies fell by 55,000
Average total pay increased by 5.8% and average regular pay increased by 6.7%
In real terms, growth in total and regular pay fell on the year
There were 556,000 working days lost because of labour disputes in March 2023.
The MPC unemployment projection for Q2 remains at 3.9% in Q2 while Trading Economics are forecasting 4.0% in Q2, unchanged from the previous forecast.
The outlook for UK unemployment can be characterised as an indifferent deterioration. This means that a higher rate of unemployment is likely at the levels projected.
The April report is due on Tuesday the 13th of June.
Sources: Office for National Statistics, Trading Economics
GEOPOLITICAL EVENTS
Russian Invasion of Ukraine
The war is having a detrimental effect on the global and UK economy by causing higher energy prices, supply chain disruptions, financial market volatility, refugee crisis and geopolitical uncertainty.
2021: 92,000 Russian troops are amassed at the Ukraine border and President Putin proposes a prohibition of Ukraine joining NATO which is rejected.
2022: On the 21st of February, President Putin ordered Russian forces to enter the separatist republics in eastern Ukraine and announced recognition of the two pro-Russian breakaway regions (Donetsk People's Republic and Luhansk People's Republic). NATO applied sanctions and scaled them up as the war progressed. Ukraine mounted a counter-offensive which regained lost territory and as winter arrived, a stalemate began.
2023: Russian began a new offensive in January although gained little ground. Ukraine is reported to be preparing for a new counteroffensive during late spring or early summer 2023.
Brexit
The UK's decision to leave the European Union (EU) has created a great deal of uncertainty about the future of the UK economy. This uncertainty has made investors less willing to take risks, which has led to a sell-off in risky assets, such as stocks and currencies.
2014-2015: The euro-sceptic party UKIP garners support and scores the most seats in the EU parliament election. The Conservatives win the 2015 general election and as promised in the manifesto, PM Cameron arranges a referendum on the UK's membership of the EU.
2016: On the 23rd of June, 52% voted for the UK to leave the EU. PM Cameron who is pro-EU resigns and Theresa May takes the helm. In October, Article 50 is triggered and the two-year process of the UK's withdrawal from the EU begins.
2017-2018: PM May calls a snap general election and loses the majority but retains power by sharing with the Democratic Unionist Party (DUP). Withdrawal agreements fail to pass parliament, an extension is made but further revisions to the agreement continue to be rejected by parliament.
2019: PM May resigns and Boris Johnson takes power who gains another extension from the EU to enable further negotiations. The deadline is now the 31st of January, 2020. Another general election is called and the Conservatives regain the majority.
2020: With negotiations strained and the deadline having passed, the UK is forced to leave the EU without a deal. Negotiations continue and a deal is eventually agreed which comes into effect on the 1st of January 2021. The EU-UK Trade and Cooperation Agreement (TCA) is a comprehensive trade deal that covers goods, services, fisheries, and much more.
MARKET NARRATIVES
Cost-of-Living Crisis
The UK cost of living crisis is having a negative effect on the value of the pound. This is because investors are becoming less confident in the UK economy and are therefore less willing to invest in British assets.
Since late 2021, the prices of essential goods have been rising faster than incomes. This has caused a fall in real income which means people now have less money to buy the things they need.
There are a number of factors that have contributed to this rise in prices, including inflation, the COVID-19 pandemic, Russia's invasion of Ukraine, and Brexit.
The UK government has taken measures to protect the most vulnerable with certain households receiving a £650 grant. All households have received a £150 council tax rebate, and an Energy Price Guarantee.
Gavin Pearson
Retail trader since 2008
Specialises in forex G7 currencies
Funded account from the5ers.com
Member of the eToro Popular Investors Program
Regular contributor to FXStreet.com analysis and education pages
Jeepson Trading Fund
Returned 27% in 2022 and 8.6% in 2023 Q1
Forex focused
Copy Trading available at eToro
eToro
eToro is a social trading platform
Users can copy trades by clicking the "Copy" button on the profile page
Disclaimer
Past performance is not indicative of future results
Trading involves risk, and you could lose money
-end-