The Euro-Area's Macroeconomic Signals
Euro-Area's economic recovery faces risks and opportunities due to Ukraine war, China's rise, and ECB's inflation-growth balance.
Sunday, 25 August, Week 35
Welcome to this comprehensive report on the macroeconomic landscape of the Euro-Area, designed to provide forex traders with valuable insights and actionable intelligence. This report delves into the intricate interplay of geopolitics, fiscal policy, economic indicators, and monetary policy, offering a holistic view of the forces shaping the Euro-Area's economic trajectory and potential trading opportunities.
In this report, we will explore the key challenges and opportunities facing the Euro-Area, including the ongoing war in Ukraine, the rise of China, and the ECB's delicate balancing act between combating inflation and supporting economic growth. We will also examine the potential impact of upcoming events, such as the release of draft budgetary plans for 2025 and the ECB's next monetary policy meeting on September 12th, on the Euro-Area's macroeconomic outlook.
By understanding the complex interplay of these factors, forex traders can gain a deeper understanding of the forces driving currency valuations and make more informed trading decisions.
Geopolitics: A Balancing Act Amidst Global Tensions
The ongoing conflict in Ukraine continues to have a far-reaching impact. It drives a wedge between Russia and Western nations and significantly increases energy prices. This has prompted a re-evaluation of defense priorities and energy security across Europe, leading to increased military spending and a search for alternative energy sources.
Beyond the immediate conflict zone, the war exacerbates geopolitical tensions. The EU's steadfast support for Ukraine, combined with stringent sanctions against Russian entities, has elicited a response from Moscow. Stratfor warns that Russia may intensify operations within Western countries, including cyberattacks and potential sabotage of critical infrastructure, to counter Western support for Ukraine. This raises concerns about heightened volatility and risk aversion in the Euro-Area, potentially impacting investor sentiment and the value of the euro.
The increasing global influence of China poses opportunities and obstacles for the Euro-Area. China's expanding economy offers European companies potential advantages, yet its assertive foreign policy raises concerns. The EU and the US are growing weary of China's dominance in crucial strategic sectors, including green and strategic technologies. This has resulted in trade tensions and tariffs. According to Stratfor, "The European Union and the United States will impose restrictions on China's green and strategic technology sectors, which may lead to retaliatory actions from China." This trade conflict could disrupt global supply chains and affect the Euro-Area's economic growth.
The Middle East, a region with far-reaching implications for the Euro-Area, continues to face volatility. The ongoing conflict between Israel and Palestine, intertwined with Iran's regional aspirations, perpetuates instability. The recent assassination of Ismail Haniyeh, Hamas' political leader, in Tehran has heightened tensions even further. Iran, along with its network of allies and proxies, is deliberating on when and where to strike Israel in retaliation for the assassination. This raises concerns of potential retaliatory attacks against Israel and even US targets within the region, potentially affecting oil prices and global risk sentiment.
Key Geopolitical Risks on the Horizon
August 26th: The PBoC will conduct its delayed MLF operation, which could provide insights into China's monetary policy stance and its potential impact on the Euro-Area.
September 6th: The US August jobs report will be released, which could influence the Fed's decision on the magnitude of a potential rate cut and indirectly impact the Euro-Area's economic outlook.
The ongoing war in Ukraine and the potential for escalation, particularly involving NATO, pose a significant risk to the Euro-Area's economic stability and energy security.
In conclusion, the geopolitical landscape surrounding the Euro-Area is fraught with uncertainty and potential risks. Forex traders need to closely monitor these developments and assess their potential impact on currency valuations.
Fiscal Policy of the Euro-Area: Recovery and Sustainability
The Euro-Area's fiscal policy is currently navigating a delicate balance between supporting economic recovery and ensuring long-term sustainability. The region is emerging from a period of unprecedented fiscal expansion in response to the COVID-19 pandemic and the energy crisis triggered by the war in Ukraine. While these measures were necessary to avert an economic collapse, they have left many countries with elevated debt levels and limited fiscal space.
Market traders are closely monitoring the implementation of the EU's reformed fiscal framework, which aims to strengthen fiscal sustainability through gradual and tailor-made adjustments complemented by reforms and investment. As stated in the July 3rd European Fiscal Board Assessment, "If strictly implemented, the new rules will put high public debt levels on a sustainable path under normal cyclical conditions." This new framework, set to be applied for the first time in the 2025 surveillance cycle, is built around a debt anchor and a single operational indicator in the form of medium-term net expenditure ceilings. The shift from a system centred on the structural budget balance of individual years to one centred on a multiannual expenditure path is intended to bring more stability to both guidance and implementation.
However, the transition to the new system is not without its challenges. The recent Commission proposal to delay the adoption of the excessive deficit recommendations has created uncertainty about the fiscal stance in 2025. The July 3rd European Fiscal Board Assessment highlights this concern: "The recent Commission proposal to delay the adoption of the excessive deficit recommendations sets a precedent, creating uncertainty around the fiscal stance in 2025." Moreover, the reformed framework's emphasis on national ownership and differentiation in debt adjustment strategies across countries has raised concerns about potential laxity and a lack of sufficient safeguards.
Upcoming Fiscal Events
The release of draft budgetary plans for 2025 later this year will provide crucial insights into national fiscal policies and their potential impact on the Euro-Area's overall fiscal stance.
The implementation of the reformed EU fiscal framework and its effectiveness in ensuring fiscal sustainability will be a key focus for market traders.
In conclusion, the Euro-Area's fiscal policy is at a crossroads. The region needs to strike a balance between supporting economic recovery and ensuring long-term fiscal sustainability. The success of the reformed EU fiscal framework in achieving this balance will be crucial for the region's economic outlook and will be closely monitored by forex traders.
Economics of the Euro-Area
Market traders are closely monitoring key economic indicators, including GDP growth, inflation, unemployment, and consumer confidence, to gauge the strength and sustainability of the recovery. The Euro-Area economy is projected to grow by 0.8% in 2024, according to the European Commission, rebounding from a 0.3% contraction in 2023. However, this growth is expected to be uneven across countries and sectors, with domestic demand picking up slowly while investment remains subdued due to high financing costs and exports are forecast to remain sluggish.
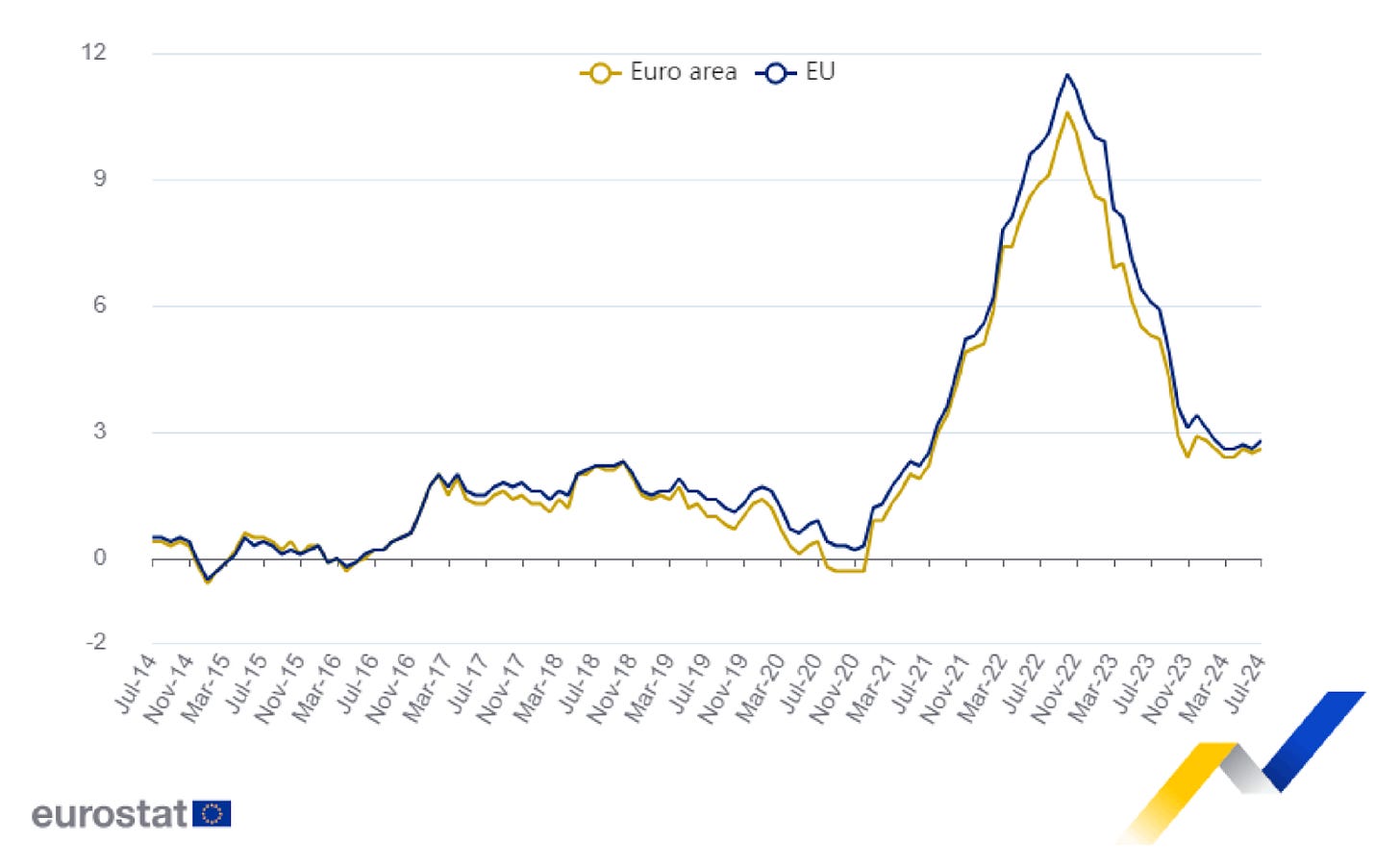
Inflation data -Eurostat
Inflation remains a key concern, with the annual inflation rate in the Euro Area at 2.6% in July 2024. While this represents a decline from the peak of 10.6% in October 2022, it is still above the ECB's 2% target. The core rate, which excludes energy, food, alcohol, and tobacco, was unchanged from the previous month at 2.9%, indicating persistent underlying inflationary pressures.
The July 2024 ECB Monetary Policy Statement notes that "domestic price pressures are still high, services inflation is elevated and headline inflation is likely to remain above the target well into next year."
The labour market has shown resilience, with the unemployment rate in the Euro Area at 6.5% in June 2024, the lowest since the start of the euro. However, the recent trend of rising unemployment, as seen in the July 2024 German unemployment data, suggests potential challenges in the coming months. The Bundesagentur für Arbeit stated that "the weak economic development is weighing on the labour market... At the beginning of the summer break, unemployment and underemployment rose more sharply than usual."
Key Economic Developments
August 26th: The release of the German Ifo Business Climate Index for August will provide further insights into business sentiment and expectations for the German economy.
The development of the labour market, particularly in light of the ongoing economic slowdown, will be a key focus for market traders.
In conclusion, the Euro-Area's economic outlook remains uncertain. While the region has shown resilience in the face of multiple shocks, challenges remain, particularly regarding inflation and the labour market. Forex traders need to closely monitor economic indicators and assess their potential impact on currency valuations.
Monetary Policy of the Euro-Area: Navigating the Shift Towards Easing
European Central Bank (ECB) in Frankfurt DE
The ECB's monetary policy is currently undergoing a significant shift, moving from an aggressive tightening cycle to a more cautious and data-dependent approach. This shift was punctuated by the ECB's decision in June 2024 to cut interest rates for the first time since the start of its tightening cycle in 2022. This move, while signalling a potential easing bias, also highlights the central bank's commitment to carefully balancing its mandate of price stability with the need to support economic growth amid a challenging geopolitical and economic environment.
The June rate cut, a reduction of 25 basis points, brought the main refinancing operations rate to 4.25%, the deposit facility rate to 3.75%, and the marginal lending rate to 4.5%. This decision, as explained in the July 18th ECB Monetary Policy Statement, was driven by several factors, including signs of moderating inflation, weak economic data, and concerns about the potential impact of the ongoing war in Ukraine and the energy crisis on economic growth.
Market traders are now closely monitoring the ECB's forward guidance and communication strategies for clues about the future path of monetary policy. The central bank has emphasised its data-dependent approach, stating that "its interest rate decisions will be based on its assessment of the inflation outlook in light of incoming economic and financial data, the dynamics of underlying inflation, and the strength of monetary policy transmission." This suggests that the ECB is prepared to further ease monetary policy if economic conditions warrant it.
"domestic price pressures are still high, services inflation is elevated and headline inflation is likely to remain above the target well into next year." -ECB Monetary Policy Statement (July)
However, the ECB is also mindful of the risks of easing too quickly, particularly given that inflation remains above its 2% target. The July 18th ECB Monetary Policy Statement noted that "domestic price pressures are still high, services inflation is elevated and headline inflation is likely to remain above the target well into next year." This suggests that the ECB will proceed cautiously with further rate cuts, carefully assessing the impact of its June decision and incoming economic data before making any further adjustments to its policy stance.
Key Monetary Policy Events
September 12th: The ECB's next monetary policy meeting will be a focal point for market traders, as the central bank is expected to provide further insights into its assessment of the economic outlook, the impact of the June rate cut, and the likely path of interest rates.
In conclusion, the ECB's monetary policy is in a state of flux, transitioning from a tightening bias to a more cautious and data-dependent approach. The June rate cut marked a significant shift in the central bank's policy stance, but the ECB remains vigilant about the risks of easing too quickly, particularly given persistent inflationary pressures. Forex traders need to closely monitor the ECB's actions and communications to anticipate potential shifts in monetary policy and their impact on currency valuations.
The Macroeconomic Outlook of the Euro-Area
The macroeconomic outlook for the Euro-Area is characterised by a cautious recovery, shaped by a complex interplay of easing monetary policy, persistent inflationary pressures, and a challenging geopolitical and economic environment. The ECB's recent shift towards a more dovish stance, marked by the June interest rate cut, has injected a dose of optimism into the outlook, but significant uncertainties remain.
Market traders are closely watching the interplay between the ECB's monetary policy easing and its potential impact on inflation and economic growth. The June rate cut, aimed at supporting economic activity, could potentially fuel inflationary pressures, particularly if not accompanied by sufficient fiscal consolidation. The ECB's data-dependent approach, however, suggests a willingness to adjust its policy stance based on evolving economic conditions, providing some reassurance to market participants.
The near-term outlook for the Euro-Area is for continued, albeit subdued, growth. The European Commission forecasts GDP growth of 0.8% in 2024, with the recovery expected to be driven by easing inflationary pressures, a resilient labour market, and a gradual fading of the negative impact from past monetary policy tightening. However, the recent contraction in the German economy in Q2 2024, as reported in the July 14th Eurostat GDP and Employment Flash Estimate, highlights the fragility of the recovery and the potential for downside risks.
In the short-term, the outlook is clouded by uncertainty, particularly regarding the trajectory of inflation and the potential for further geopolitical and economic shocks. The ECB's monetary policy easing cycle, while intended to support economic activity, could potentially fuel inflationary pressures, particularly if not accompanied by sufficient fiscal consolidation. Additionally, the ongoing war in Ukraine and the potential for escalation pose a significant risk to the Euro-Area's economic stability and energy security.
The mid-term outlook hinges on the effectiveness of the ECB's monetary policy easing in stimulating economic growth without reigniting inflation. The success of structural reforms and investment aimed at boosting productivity and competitiveness will also be crucial for the region's long-term economic prospects. The implementation of the EU's reformed fiscal framework, which aims to strengthen fiscal sustainability, will also play a key role in shaping the mid-term outlook.
The risks to the Euro-Area's macroeconomic outlook are significant and multifaceted. A prolonged war in Ukraine, a sharp slowdown in global growth, or a resurgence of inflationary pressures could derail the recovery. Additionally, political instability in key Euro-Area countries, such as Italy and France, could undermine confidence and weigh on economic activity.
In conclusion, the Euro-Area's macroeconomic outlook is characterised by a cautious recovery, shaped by a complex interplay of easing monetary policy, persistent inflationary pressures, and a challenging geopolitical and economic environment. The ECB's shift towards a more dovish stance has injected a dose of optimism into the outlook, but significant uncertainties remain. Forex traders need to carefully assess these risks and their potential impact on currency valuations, particularly in light of the ECB's upcoming monetary policy meeting on September 12th.
Economic Indicators of the Euro-Area
Economic Growth
GDP Growth Rate: The Euro-Area GDP expanded 0.30 percent in the second quarter of 2024 over the previous quarter. GDP Growth Rate in Euro Area is expected to be 0.30 percent by the end of this quarter, according to Trading Economics global macro models and analysts expectations. In the long-term, the Euro Area GDP Growth Rate is projected to trend around 0.40 percent in 2025 and 0.30 percent in 2026, according to our econometric models. In the short term, the Eurostat flash estimate for Q2 GDP growth was revised upwards from 0.6% to 0.8% for the EU, suggesting a slightly stronger recovery than initially anticipated. However, the German economy unexpectedly contracted by 0.1% in Q2, highlighting the uneven nature of the recovery across the Euro-Area. In the mid-term, the outlook for GDP growth remains subject to significant uncertainty, particularly due to the ongoing war in Ukraine, the potential for further energy price shocks, and the impact of the ECB's monetary policy tightening cycle.
Industrial Production MoM: Industrial Production In the Euro Area decreased 0.10 percent in June of 2024 over the previous month. Industrial Production Mom in Euro Area averaged 0.08 percent from 1990 until 2024, reaching an all time high of 13.50 percent in May of 2020 and a record low of -18.60 percent in April of 2020. In the short term, the German industrial production data for June showed a positive surprise, with output rising by 1.4% month-over-month, beating market consensus of 1.0%. This suggests that the German industrial sector may be more resilient than initially anticipated. However, the mid-term outlook for industrial production remains clouded by uncertainty, particularly due to the ongoing war in Ukraine, the potential for further energy price shocks, and the impact of the ECB's monetary policy tightening cycle.
Price Changes (Inflation)
Inflation Rate: Inflation Rate In the Euro Area increased to 2.60 percent in July from 2.50 percent in June of 2024. Inflation Rate in Euro Area is expected to be 2.20 percent by the end of this quarter, according to Trading Economics global macro models and analysts expectations. In the long-term, the Euro Area Inflation Rate is projected to trend around 2.10 percent in 2025, according to our econometric models. In the short term, the Eurostat flash estimate for July inflation showed a slight upward revision from 2.4% to 2.6%, indicating that inflationary pressures may be proving more persistent than initially anticipated. In the mid-term, the outlook for inflation remains subject to significant uncertainty, particularly due to the potential for second-round effects from wage growth, the ongoing war in Ukraine, and the impact of the ECB's monetary policy tightening cycle.
Core Inflation Rate: Core consumer prices In the Euro Area increased 2.90 percent in July of 2024 over the same month in the previous year. Core Inflation Rate in Euro Area is expected to be 2.40 percent by the end of this quarter, according to Trading Economics global macro models and analysts expectations. In the long-term, the Euro Area Core Inflation Rate is projected to trend around 2.00 percent in 2025, according to our econometric models. In the short term, the Eurostat flash estimate for July core inflation confirmed the preliminary estimate of 2.9%, indicating persistent underlying inflationary pressures. In the mid-term, the outlook for core inflation remains subject to significant uncertainty, particularly due to the potential for second-round effects from wage growth, the ongoing war in Ukraine, and the impact of the ECB's monetary policy tightening cycle.
Labour
Unemployment Rate: Unemployment Rate In the Euro Area increased to 6.50 percent in June from 6.40 percent in May of 2024. Unemployment Rate in Euro Area averaged 9.30 percent from 1995 until 2024, reaching an all time high of 12.20 percent in January of 2013 and a record low of 6.40 percent in April of 2024. In the short term, the German unemployment rate rose to 6% in July, the highest since May 2021, indicating potential weakness in the labor market. The mid-term outlook for the unemployment rate remains subject to uncertainty, particularly due to the ongoing economic slowdown and the potential for further job losses in the manufacturing and services sectors.
Employment Change: The number of employed persons increased by 18 thousand to 2.802 million in July 2024, marking a 19th consecutive period of rising unemployment, surpassing forecasts of 15 thousand. Unemployment Change in Germany averaged 0.05 Thousand from 1992 until 2024, reaching an all time high of 355.00 Thousand in April of 2020 and a record low of -96.00 Thousand in May of 2006. In the short term, the Eurostat flash estimate for Q2 employment growth showed a slowdown in both the euro area and the EU, with employment increasing by 0.2% compared with the previous quarter. This suggests that the labor market may be losing momentum. In the mid-term, the outlook for employment growth remains subject to uncertainty, particularly due to the ongoing economic slowdown and the potential for further job losses in the manufacturing and services sectors.
Business Confidence
ZEW Economic Sentiment Index: The ZEW Indicator of Economic Sentiment for the Euro Area continued to plummet in August 2024, dropping 25.8 points to a nine-month low of 17.9, well below forecasts of 35.4. It marks the second consecutive month of deterioration in the morale gauge, amid ongoing uncertainty about the economic outlook and the direction of monetary policies. In August, about 54.3 percent of the surveyed analysts expected no changes in economic activity, 31.8 percent predicted an improvement and 13.9 percent anticipated a deterioration. In the meantime, the indicator of the current economic situation rose by 3.7 points to -32.4 and inflation expectations went up by 2 points to -39.1. In the short term, the ZEW Economic Sentiment Index for Germany plunged to 19.2 in August 2024 from 41.8 in July, the lowest in seven months and well below market expectations of 32. This marked a significant 22.6 point decline from July, the largest plummet since July 2022. The mid-term outlook for business confidence remains clouded by uncertainty, particularly due to the ongoing war in Ukraine, the potential for further energy price shocks, and the impact of the ECB's monetary policy tightening cycle.
Ifo Business Climate Index: The Ifo Business Climate indicator for Germany declined for a third consecutive month to 87 in July 2024, the lowest since February, from 88.6 in June and forecasts of 88.9. Sentiment has declined considerably at companies in Germany, with both current conditions (87.1 vs 88.3) and expectations (86.9 vs 88.8) worsening. In the short term, the Ifo Business Climate Index is expected to rebound to 91.00 points by the end of this quarter. However, the mid-term outlook for business confidence remains clouded by uncertainty, particularly due to the ongoing war in Ukraine, the potential for further energy price shocks, and the impact of the ECB's monetary policy tightening cycle.
Consumer Sentiment
Consumer Confidence: The GfK Consumer Climate Indicator for Germany climbed to -18.4 heading into August 2024 from a marginally revised -21.6 in the previous period, above market estimates of -21.0. It was the highest reading since April 2022, amid easing cost pressures and rising wages. Income expectations were significantly higher (19.7 vs 8.2 in July), notching their highest level in nearly 3 years. Also, there were rises in economic prospects (9.8 vs 2.5) and the propensity to buy (-8.4 vs -13.0). Meanwhile, the tendency to save was almost unchanged. In the short term, the GfK Consumer Climate Indicator for Germany is expected to decline to -22.00 points by the end of this quarter. However, the mid-term outlook for consumer confidence remains subject to uncertainty, particularly due to the ongoing economic slowdown and the potential for further job losses in the manufacturing and services sectors.
Economic Sentiment Indicator: The economic sentiment indicator in the Euro Area eased marginally to 95.8 in July of 2024 from 95.9 in the previous month, but ahead of market expectations of 95.4. Still, the drop pointed to the greatest extent of pessimism in the Eurozone’s economy since February, aligning with the European Central Bank’s decision to commence easing monetary and financial restrictions in the currency bloc. Sentiment worsened for both industry (-10.5 vs -10.2 in June) and services (4.8 vs 6.2), while pessimism for consumers softened (-13 vs -14). In the short term, the Economic Sentiment Indicator is expected to remain around current levels. However, the mid-term outlook for consumer sentiment remains subject to uncertainty, particularly due to the ongoing economic slowdown and the potential for further job losses in the manufacturing and services sectors.
Trade
Balance of Trade: Euro Area recorded a trade surplus of 22334.60 EUR Million in June of 2024. Balance of Trade in the Euro Area averaged 5565.80 EUR Million from 1999 until 2024, reaching an all time high of 29946.10 EUR Million in July of 2015 and a record low of -55033.30 EUR Million in August of 2022. In the short term, the German trade surplus declined to EUR 20.4 billion in June 2024 from an upwardly revised EUR 25.3 billion in June, smaller than forecasts of EUR 23.5 billion. It was the smallest trade surplus since last October, as exports dropped while imports grew. In the mid-term, the outlook for the Euro-Area's trade balance remains subject to uncertainty, particularly due to the ongoing war in Ukraine, the potential for further energy price shocks, and the impact of the ECB's monetary policy tightening cycle.
Exports: Exports from Germany dropped by 3.4% month-over-month to a six-month low of EUR 127.7 billion in June 2024, worse than market forecasts of a 1.5% drop, following a downwardly revised 3.1% fall in the previous month, the steepest decline since last December. Shipments to the EU fell by 3.4%, dragged by those from the Euro area (-3.2%) and non-Euro area (-3.7%). Also, exports to third countries dropped by 3.5%, with exports to the US shrinking by 7.7%, while those to the UK, and Russia fell by 0.6% and 3.2%, respectively. By contrast, exports to China rose by 3.4%. For the first seven months of 2024, exports fell 1.1% compared with the corresponding period last year to EUR 798.8 billion. In the short term, German exports are expected to decline further, with the balance of trade forecast to reach EUR 18.00 Billion by the end of this quarter. In the mid-term, the outlook for Euro-Area exports remains subject to uncertainty, particularly due to the ongoing war in Ukraine, the potential for further energy price shocks, and the impact of the ECB's monetary policy tightening cycle.
Conclusion: Charting a Profitable Course in the Euro-Area's Macroeconomic Landscape
The Euro-Area's macroeconomic landscape presents a complex and dynamic environment for forex traders. The region is navigating a path to recovery, but one that is fraught with risks and opportunities. The ongoing war in Ukraine, the rise of China, and the ECB's delicate balancing act between combating inflation and supporting economic growth all have the potential to significantly impact the Euro-Area's economic trajectory and, consequently, currency valuations.
Key takeaways for forex traders:
Monitor the impact of the ECB's easing cycle: The ECB's shift towards a more dovish stance, marked by the June interest rate cut, has injected a dose of optimism into the outlook, but the potential impact on inflation and economic growth needs to be carefully monitored. Pay close attention to the ECB's next monetary policy meeting on September 12th for further insights into its assessment of the economic outlook, the impact of the June rate cut, and the likely path of interest rates.
Stay informed about fiscal policy decisions: The implementation of the EU's reformed fiscal framework and its effectiveness in ensuring fiscal sustainability will be crucial for the region's long-term economic prospects. The release of draft budgetary plans for 2025 later this year will provide crucial insights into national fiscal policies and their potential impact on the Euro-Area's overall fiscal stance.
Track economic indicators: Closely monitor key economic indicators, such as GDP growth, inflation, unemployment, and consumer confidence, to gauge the strength and sustainability of the recovery. Pay close attention to the release of the German Ifo Business Climate Index on August 26th, the Australian CPI on August 28th, Nvidia's earnings on August 29th, and the US PCE data on August 30th.
Assess geopolitical risks: The ongoing war in Ukraine, the rise of China, and the volatile situation in the Middle East all have the potential to significantly impact the Euro-Area's economic outlook and drive currency volatility. Pay close attention to developments surrounding the PBoC's MLF operation on August 26th and the US jobs report on September 6th.
By staying informed about these key factors and their potential impact on currency valuations, forex traders can navigate the Euro-Area's macroeconomic landscape and chart a profitable course.
Sources
European Central Bank
European Commission
Eurostat
Federal Statistical Office, Germany
INSEE, France
Trading Economics
Bloomberg
Reuters
OECD
IMF
GfK Group
Ifo Institute
Centre for European Economic Research (ZEW)
S&P Global
Ministère de l'Économie et des Finances, France
Bundesagentur für Arbeit, Germany
DARES, France
Newsquawk
Stratfor Worldview