The United States: A Cooling Economy and Shifting Monetary Policy Expectations
Saturday, 29 June, Week 26: The US economy is navigating a period of transition, marked by slowing growth, easing inflation, and a robust labour market. While economic activity has cooled from the highs of last year, it remains resilient, supported by strong consumer spending and a gradual easing of supply chain disruptions. The Federal Reserve, after a series of interest rate hikes, has opted to pause its tightening cycle, but the path of monetary policy remains uncertain as policymakers closely monitor incoming data for signs of sustained disinflation. Geopolitical tensions, particularly with China, and the upcoming US presidential election are adding to market volatility, creating both opportunities and challenges for investors.
Fiscal Policy
The US fiscal policy stance has been relatively neutral over the past five months. The government has continued to provide support to the economy through spending programs, but it has also taken steps to reduce the budget deficit. The recent passage of the Fiscal Responsibility Act of 2023, which suspended the debt limit through January 1, 2025, has removed a major source of uncertainty for the markets. However, the law also includes spending caps that could constrain the government's ability to respond to economic shocks in the coming years.
Looking ahead, the fiscal policy outlook is likely to be shaped by the upcoming presidential election. The Biden administration has proposed a budget that includes significant investments in infrastructure, education, and clean energy, but it is unclear whether these proposals will be enacted by Congress. The outcome of the election could also have a significant impact on the future direction of fiscal policy, with the potential for either more expansionary or more restrictive policies depending on which party wins.
Economics
The US economy has shown signs of cooling in recent months, but it remains fundamentally strong. Consumer spending, which accounts for about two-thirds of economic activity, has slowed from the robust pace of last year, but it remains solid. Business investment has also moderated, but it is being supported by strong corporate profits and low interest rates. The housing market, however, has been hit hard by rising mortgage rates, with sales and construction activity declining sharply.
The economic outlook for the next five weeks is for continued moderate growth. Consumer spending is expected to remain resilient, supported by a strong labour market and easing inflation. Business investment is also likely to pick up, as companies take advantage of low interest rates and tax incentives. The housing market, however, is expected to remain weak, as high mortgage rates continue to weigh on demand.
Economic Growth
The US economy expanded by an annualised 1.4% in the first quarter of 2024, a significant slowdown from the 3.4% growth in the fourth quarter of 2023. The slowdown was driven by a sharp decline in consumer spending on goods, which was partly offset by strong growth in business investment and government spending. The third estimate of GDP growth was slightly higher than the second estimate, reflecting upward revisions to nonresidential fixed investment and government spending.
Looking ahead, economic growth is expected to remain moderate in the second quarter of 2024. The Atlanta Fed's GDPNow model is currently forecasting 1.5% growth, while the consensus forecast is for 1.8% growth. The economy is facing a number of headwinds, including high inflation, rising interest rates, and ongoing supply chain disruptions. However, it is also being supported by a strong labour market and pent-up consumer demand.
Labour
The US labour market remains very strong, with the unemployment rate falling to a multi-decade low of 3.4% in April 2024. The number of unemployed persons decreased by 21,000 to 5.894 million in April, while employment levels increased by 1.1 million to 161.59 million. The labour force participation rate increased to 62.5% from 62.2% in March.
In May, the unemployment rate ticked up to 4%, with the number of unemployed persons increasing by 157,000 to 6.649 million. Employment levels decreased by 408,000 to 161.083 million. The labour force participation rate dropped to 62.5% from 62.7%, and the employment-population ratio decreased to 60.1% from 60.2%.
The labour market is expected to remain strong in the coming weeks, with continued job growth and low unemployment. The Conference Board's Employment Trends Index, a leading indicator of labour market conditions, rose to 118.5 in May, suggesting that the labour market is likely to remain strong in the near term.
Price Changes
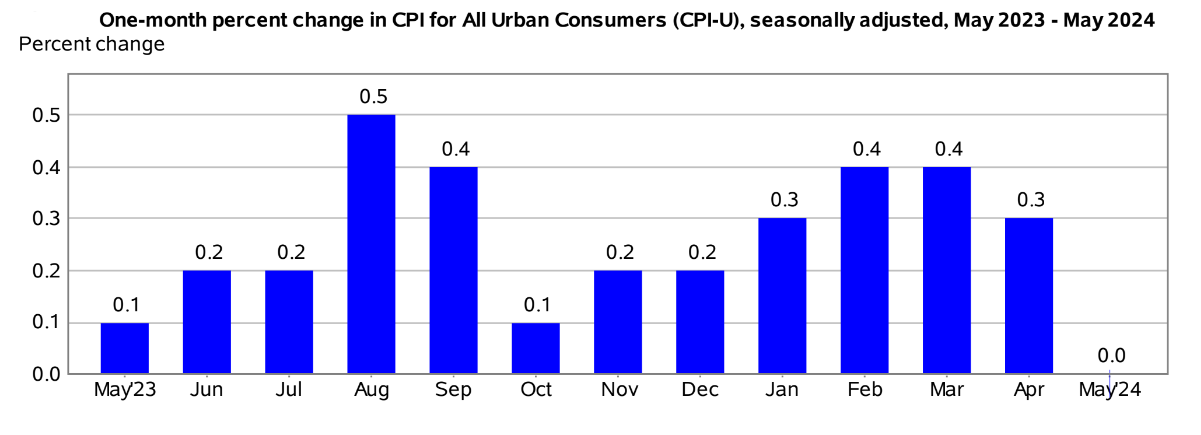
Inflation in the US has been moderating in recent months, but it remains elevated. The Consumer Price Index (CPI) rose 3.3% year-on-year in May 2024, the smallest increase in three months, compared to 3.4% in April. Core inflation, which excludes food and energy prices, slowed to 3.4% annually, the lowest rate since April 2021.
The slowdown in inflation was driven by a decline in gasoline prices, which fell 3.6% in May. However, shelter costs continued to rise, increasing 0.4% for the fourth consecutive month. Food prices also edged up 0.1% in May.
Inflation is expected to continue to moderate in the coming weeks, as supply chain disruptions ease and the Federal Reserve's interest rate hikes take effect. The Cleveland Fed's Median CPI, a measure of underlying inflation, rose 0.2% in May, suggesting that inflation is likely to remain moderate in the near term.
Trade
The US trade deficit widened to $74.6 billion in April 2024, the largest since October 2022. The increase in the deficit was driven by a surge in imports, which rose 8.7% to $338.2 billion. Exports edged up a meagre 0.8% to $263.7 billion.
The widening trade deficit is a sign of strong domestic demand, as US consumers and businesses continue to purchase goods and services from abroad. However, it is also a drag on economic growth, as it subtracts from GDP.
The trade deficit is expected to remain elevated in the coming weeks, as domestic demand remains strong and the dollar remains strong. The strong dollar makes US exports more expensive for foreign buyers and imports cheaper for US buyers.
Monetary Policy
The Federal Reserve has paused its interest rate hiking cycle after raising the fed funds target range to 5.25%-5.50% in June 2024. The Fed has signaled that it is likely to keep interest rates at this level for some time, as it assesses the impact of its previous rate hikes on the economy.
The Fed's dot plot, which shows policymakers' projections for the future path of interest rates, now signals one rate cut in 2024 and four rate cuts in 2025.
The Fed's decision to pause its rate hiking cycle and to reduce the number of projected rate cuts reflects concerns about persistent inflation. The Fed's preferred measure of inflation, the PCE price index, was revised higher for 2024 and 2025 in the June Summary of Economic Projections. The FOMC noted:
"The Committee judges that the risks to achieving its employment and inflation goals have moved toward better balance over the past year. The economic outlook is uncertain, and the Committee remains highly attentive to inflation risks...The Committee does not expect it will be appropriate to reduce the target range until it has gained greater confidence that inflation is moving sustainably toward 2 percent." - Federal Open Market Committee, June 12, 2024
The Fed is likely to remain data dependent in its monetary policy decisions in the coming weeks. If inflation continues to moderate, the Fed could begin to cut interest rates later this year. However, if inflation remains elevated, the Fed could keep interest rates at their current level or even raise them further.
Geopolitics and Market Themes
US Presidential Election
The US presidential election is scheduled for November 5, 2024. The race is expected to be close, with former President Donald Trump challenging incumbent President Joe Biden. The outcome of the election could have a significant impact on the US economy and financial markets.
Trump has pledged to implement a number of policies that could boost economic growth, such as tax cuts and deregulation. However, he has also proposed policies that could increase inflation, such as tariffs on imports from China.
Biden has pledged to continue his current economic policies, which include investments in infrastructure, education, and clean energy. However, he is facing headwinds from high inflation and rising interest rates.
The uncertainty surrounding the election is likely to contribute to market volatility in the coming months. Investors will be closely watching the polls and the debates for clues about the likely outcome of the race.
China-US Trade Tensions
Trade tensions between the United States and China have escalated in recent years, as the two countries have imposed tariffs on each other's goods. The trade war has had a negative impact on both economies, disrupting supply chains and raising prices for consumers.
The Biden administration has maintained most of the tariffs that were imposed by the Trump administration, but it has also engaged in talks with China to try to resolve the trade dispute. However, progress in the talks has been slow, and tensions remain high. The trade war is likely to continue to weigh on the US economy in the coming months. The tariffs are raising costs for US businesses and consumers, and they are also contributing to uncertainty about the future of the global economy.
Russia-Ukraine War
The war in Ukraine, which began in February 2022, has had a significant impact on the global economy. The war has disrupted supply chains, raised energy prices, and increased geopolitical tensions.
The United States and its allies have imposed sanctions on Russia in an effort to pressure Moscow to end the war. However, the sanctions have had a limited impact on the Russian economy, and the war is likely to continue for some time.
The war in Ukraine is likely to continue to weigh on the US economy in the coming months. The war is contributing to uncertainty about the future of the global economy, and it is also raising the risk of a wider conflict.
Israel-Hezbollah Clashes
Tensions between Israel and Hezbollah have escalated in recent weeks, as the two sides have exchanged fire across the Lebanon-Israel border. The clashes have raised concerns about a wider conflict, which could have a significant impact on the global economy.
The United States has called for a de-escalation of tensions, but it has also provided military support to Israel. Iran, which backs Hezbollah, has warned Israel against any attack on Lebanon.
The clashes between Israel and Hezbollah are likely to continue to be a source of uncertainty in the coming weeks.
OTHER NEWS
Amazon Launches a Rival to Shein and Temu: Amazon is setting up a discounted shop that will fly products to consumers from China, utilising a trade loophole called de minimis. The move is a direct challenge to Shein and Temu, two Chinese companies that have exploded onto the retail scene over the past few years by offering startlingly cheap items.
Walgreens Plans to Shutter Stores and Refocus after Weak Earnings: After missing its third-quarter earnings and slashing its full-year outlook, Walgreens is planning to close a substantial number of US locations. The move comes as pharmacies have struggled to make their push into medical care profitable.
OECD Report Highlights Teenagers' Lack of Financial Literacy: Nearly a fifth of teenagers in advanced economies lack the baseline financial literacy and math skills to make simple everyday money decisions, according to a new report by the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development.
Conclusion
The US economy is in a period of transition, with slowing growth, easing inflation, and a strong labour market. The Federal Reserve has paused its interest rate hiking cycle, but the path of monetary policy remains uncertain. Geopolitical tensions, particularly with China, and the upcoming US presidential election are adding to market volatility.
For forex traders, the outlook for the US dollar is uncertain. The dollar is likely to be influenced by a number of factors, including the path of monetary policy, the outcome of the presidential election, and the evolution of geopolitical tensions.
References
Federal Reserve:
https://www.federalreserve.gov/
U.S. Bureau of Economic Analysis:
https://www.bea.gov/
U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics:
https://www.bls.gov/
U.S. Census Bureau:
https://www.census.gov/
Trading Economics:
https://tradingeconomics.com/
The Information:
https://www.theinformation.com/
Business Insider:
https://www.businessinsider.com/
The Wall Street Journal:
https://www.wsj.com/
Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development:
https://www.oecd.org/
Reuters:
https://www.reuters.com/
Bloomberg:
https://www.bloomberg.com/
Stratfor:
https://worldview.stratfor.com/
CFTC:
https://www.cftc.gov/