Turbulent Markets as Central Banks Shift Gears
FOREX TRADERS REFERENCE: your regularly updated guide to the currency markets
DERBYSHIRE UK, Dec 28, 2023, Week 52. Welcome to the last lap of the year and a small bit of housekeeping to begin with as the weekly update will now be known as the Forex Traders Reference. Designed to be your go-to briefing, the aim is to deliver frequent, sharp, to-the-point insights tailored to serve as a handy reference. Paid-subscribers will also continue to receive full access to the Trade Plans which are more vital hen ever as Central Banks gear up for their dovish turns in 2024
In the United States, a narrative of cooling inflation and anticipated Federal Reserve rate cuts is pushing the US Dollar to near five-month lows, while robust GDP growth and low unemployment suggest underlying resilience. Across the pond, the Euro-Area grapples with high inflation and a slight GDP contraction, yet a decrease in inflation and positive spending indicators provide a glimmer of resilience, influencing the Euro's strength against the dollar. The UK's story is one of balancing act with persistent inflationary pressures and a contracting GDP, countered by a tight labour market and the anticipation of rate cuts, shaping the trajectory of the Pound-Sterling. Over in Japan, a mix of economic contraction and a tight labour market, coupled with the Bank of Japan's ultra-loose monetary policy, sets the stage for the Japanese Yen's performance. As we step into 2024, key economic events and policy decisions will undoubtedly play pivotal roles in guiding these currencies, offering both challenges and opportunities for the astute trader.
Trading involves a possibility of losing money therefore all decisions in market speculation are undertaken at your own financial risk.
Macroeconomics
UNITED-STATES: The performance of the U.S. economy has been subject to both headwinds and tailwinds, shaping a complex narrative for the US Dollar. Headwinds include a deceleration in economic growth and job gains, alongside persistent but cooling inflation, suggesting an economy poised between growth and emerging pressures. Conversely, tailwinds come from robust GDP growth, the strongest since Q4 2021, and a low unemployment rate, signalling underlying economic resilience. These dynamics have led to a narrative of cooling inflation and anticipated Federal Reserve rate cuts, pushing the US Dollar to near five-month lows. Trading Economics forecasts a gradual reduction in the federal funds rate and a continued but slower growth trajectory for the economy, suggesting a potentially softer dollar as lower rates might diminish its yield appeal. However, if inflation and employment maintain a steady but improved course as predicted, it could mitigate severe downside risks for the dollar, ensuring a balanced economic and monetary environment. The interplay between these factors will be crucial in shaping the future direction of the US Dollar and the broader economic landscape.
EURO-AREA: The Euro-Area economy has navigated through a mix of headwinds and tailwinds, significantly shaping the narrative around the Euro. On the one hand, persistent high inflation and a slight contraction in GDP during Q3 2023 underscore economic challenges and represent headwinds, prompting the European Central Bank (ECB) to maintain high interest rates and signal the end of its bond purchase scheme. Such restrictive monetary policy, aimed at combating inflation, theoretically supports the Euro's strength. However, the reality of subdued consumer demand, as evidenced by stagnant retail sales, along with a steady unemployment rate, adds complexity by dampening growth prospects. These economic struggles are juxtaposed with tailwinds from a decreasing annual inflation rate and positive consumption and public spending indicators, suggesting some resilience in the economy. The Euro's direction has been influenced by the narrative around the ECB's more aggressive stance on inflation compared to the Federal Reserve's projected rate cuts, contributing to its strengthening against the dollar. Trading Economics forecasts suggest a gradual easing of inflation and a moderate unemployment rate, which, if realised, could stabilise the economy and potentially support the Euro. However, any deviation from these predictions, particularly if inflation remains stubbornly high or growth continues to falter, could exert downward pressure on the Euro and worsen the economic outlook.
UNITED-KINGDOM: The UK economy is navigating through various headwinds and tailwinds, influencing the narrative around the Pound-Sterling. Persistent inflationary pressures and a contracting GDP in Q3 2023 represent significant headwinds, prompting the Bank of England to maintain interest rates at a 15-year high. The tight labour market and the threat of sustained inflation suggest ongoing economic strain, potentially supporting a strong Pound in the short term due to high-interest rates. However, the anticipation of rate cuts by both the Federal Reserve and the Bank of England in 2024, amid softening inflation and economic slowdown, creates a tailwind, fostering optimism and contributing to the Pound's stabilisation. Trading Economics forecasts a gradual decrease in the UK interest rate and a slow improvement in economic indicators like inflation and unemployment. If these projections materialise, the anticipated rate cuts could weaken the Pound as lower rates might reduce its yield appeal. However, if the economy shows resilience and inflation is controlled without significant harm to growth, it could support a more stable and possibly stronger Pound. The balance between these factors and global economic shifts will be crucial in shaping the future trajectory of the Pound-Sterling and the UK economy.
JAPAN: The Japanese economy has been navigating through a combination of headwinds and tailwinds, influencing the narrative and performance of the Japanese Yen. Headwinds include a contraction in Q3 2023 GDP, reflecting domestic economic challenges such as decreased private consumption and capital expenditures, alongside global economic pressures. Additionally, inflation rates remain above the Bank of Japan's (BoJ) 2% target, indicating persistent cost pressures. These factors have led the BoJ to maintain its ultra-loose monetary policy, with negative interest rates and a commitment to continue monetary easing, which traditionally weakens the Yen. However, there are also tailwinds, such as a stable unemployment rate and a jobs-to-applications ratio indicating a tight labour market, which can be supportive of the economy and potentially the Yen. The inflation rate's slight decrease and the central bank's cautious approach also suggest an eventual normalisation path that might strengthen the currency. Trading Economics forecasts a slight uptick in the interest rate and a modest recovery in GDP growth. If these projections materialise, they might signal a gradual improvement in the economy and could lead to a stronger Yen. However, if economic recovery is slower than expected or inflation remains stubbornly high, it could necessitate continued or intensified monetary easing, potentially exerting further downward pressure on the Yen.
Currency Pairs
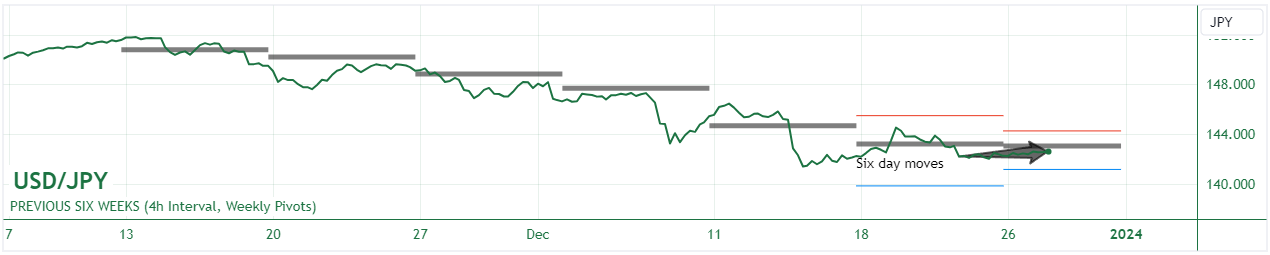
USD/JPY: Over the short term, the USD/JPY has remained steady since December 21st, reflecting a balance between contrasting monetary policies and economic outlooks in the United States and Japan. The US Dollar's narrative has been dominated by cooling inflation and market anticipation of Federal Reserve rate cuts next year, pulling the currency closer to five-month lows. This anticipation of easing has likely been tempered in the short term by other factors such as end-of-year market positioning and a wait-and-see approach leading up to more definitive action from the Fed. Meanwhile, the Japanese Yen's narrative has been shaped by the Bank of Japan's (BoJ) continued ultra-loose monetary policy and a lack of clear signals towards policy normalisation. This stance, combined with a contraction in Japan's GDP and persistent inflation above the BoJ's target, has traditionally weakened the Yen. However, the BoJ's reaffirmation of its dovish stance, juxtaposed with the Fed's anticipated rate cuts, has likely contributed to the Yen's relative stability against the Dollar in the short term.
Over the long term, since November 15th, the USD/JPY has lost value, largely due to the evolving economic narratives and market expectations in both countries. The gradual shift in the US narrative towards a softer stance on interest rates in response to cooling inflation has likely led to a reevaluation of the Dollar's strength. As markets price in the likelihood of rate cuts, the Dollar's appeal diminishes, contributing to its long-term decline against the Yen. Concurrently, while the Japanese Yen has been under pressure from the BoJ's dovish policies, any signs of economic stability or hints towards future policy shifts could provide the Yen with some support. The BoJ's recent discussions on the potential timing of ending negative interest rates, while not indicating immediate action, may have introduced a cautious optimism about Japan's monetary policy future, contributing to the Yen's strength against the Dollar over the longer term. This intricate interplay between the cooling US inflation expectations and Japan's sustained loose monetary stance has thus shaped the recent trajectory of the USD/JPY.
Here are some key events to watch in relation to the USD/JPY:
Wednesday, January 03, 2024 - US ISM Manufacturing PMI (DEC): This measure of manufacturing health can indicate economic strength or weakness. A higher than expected PMI could strengthen the USD as it suggests economic resilience, possibly impacting the USD/JPY by reflecting a diverging economic path compared to Japan's.
Friday, January 05, 2024 - US Non-Farm Payrolls (DEC): This key indicator of employment health is closely watched. Higher employment numbers could suggest continued economic strength in the US, potentially leading to a stronger USD against the JPY if the Japanese economy isn't showing similar strength.
Thursday, January 11, 2024 - US Core Inflation Rate YoY (DEC): Inflation is a critical component in Federal Reserve decision-making. If inflation cools more than expected, it could reinforce the narrative of impending Fed rate cuts, potentially weakening the USD against the JPY.
Thursday, January 04, 2024 - JP Jibun Bank Manufacturing PMI Final (DEC): This data provides insight into the health of the Japanese manufacturing sector. A stronger than expected PMI could suggest economic resilience in Japan, potentially strengthening the JPY against the USD.
Friday, January 12, 2024 - JP Current Account (NOV): As an indicator of Japan's international economic position, a higher than expected surplus might reflect well on Japan's economic health, possibly strengthening the JPY against the USD, especially if the US economic data around the same time shows weakness or uncertainty.
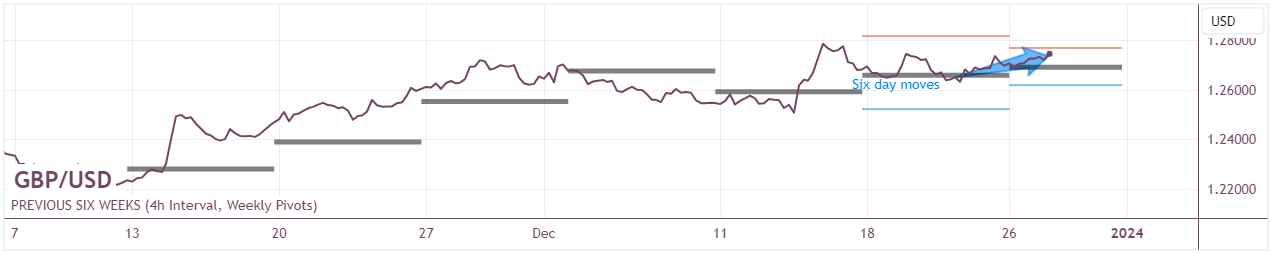
GBP/USD: Over the short term, the GBP/USD has gained a little value since December 21, primarily due to the contrasting narratives surrounding both currencies. The Pound has been supported by the narrative of anticipated Bank of England rate cuts amid an environment of softening inflation and economic slowdown, which, while suggesting possible future weakness, currently underpins the currency due to the high-interest rates still in place. Simultaneously, the US Dollar has been influenced by cooling inflation and increasing market bets on the Federal Reserve starting interest rate cuts in the next year, leading to its position near five-month lows. This expectation of a looser monetary policy in the US compared to the UK's cautious stance has slightly tipped the scale in favour of the Pound in the short term. Over the long term, since November 15, the GBP/USD has gained value, largely due to the broader narrative surrounding both economies. The US Dollar has faced sustained pressure from a market increasingly confident in the Federal Reserve's shift towards rate cuts in response to cooling inflation, decreasing the currency's yield appeal. Conversely, while the UK also faces the prospect of rate cuts, the Pound has benefited from a relatively more hawkish Bank of England and persistent inflationary pressures, which have delayed an aggressive shift in policy. This relative difference in monetary policy outlooks and the stronger start position due to higher rates in the UK have contributed to the Pound's longer-term appreciation against the Dollar.
Here are some key events to watch in relation to the GBP/USD:
Friday, January 12, 2024, GB GDP MoM NOV: This report on the UK's Gross Domestic Product for November will provide insight into the economic growth or contraction during the period. A stronger than expected growth rate could bolster the Pound by suggesting resilience in the UK economy, potentially influencing the Bank of England's stance on interest rates.
Friday, January 12, 2024, GB Goods Trade Balance NOV: This data indicates the difference in value between imported and exported goods during November. A narrowing deficit or a surplus could strengthen the Pound by reflecting a healthier economic condition, while a widening deficit might weaken it.
Friday, January 05, 2024, US Non-Farm Payrolls DEC: This crucial employment report provides insights into the health of the US labour market. Strong job growth could signal economic resilience, potentially supporting the Dollar, while weak figures might fuel expectations for more aggressive Federal Reserve rate cuts.
Thursday, January 11, 2024, US Core Inflation Rate YoY DEC: This measure of inflation, excluding volatile food and energy prices, will offer clues about underlying inflationary pressures in the US. Higher than expected inflation could temper expectations for Fed rate cuts, supporting the Dollar, while lower figures might enhance the case for easing and weigh on the currency.
Wednesday, January 03, 2024, US FOMC Minutes: The release of the minutes from the Federal Open Market Committee's latest meeting will provide deeper insights into the Fed's monetary policy outlook. Any signals indicating a shift in stance towards rate cuts or concern over economic conditions could significantly impact the Dollar's strength and, consequently, the GBP/USD pair.
EUR/USD: Over the short term, the EUR/USD has gained value since December 21, primarily due to the contrasting monetary policy outlooks between the European Central Bank (ECB) and the Federal Reserve. The Euro has been bolstered by expectations that the ECB will cut rates more slowly and cautiously compared to the more aggressive anticipated cuts by the Federal Reserve, a scenario underscored by the recent dip in U.S. core PCE inflation to 3.2%, confirming the cooling inflation narrative. This divergence enhances the Euro's appeal relative to the Dollar, particularly as markets price in an 80% chance of a Federal Reserve rate reduction as early as March 2024. Over the long term, since November 15, the EUR/USD has also gained value, reflecting a sustained trend of Dollar weakness amid firm market expectations of significant rate cuts in the upcoming year to address slowing inflation. Meanwhile, the Euro has found support from a relatively hawkish ECB stance and better-than-expected economic resilience in the Euro-Area, despite challenges. This comparative dynamic, along with the broader narrative of the Federal Reserve’s anticipated easing cycle outpacing the ECB's actions, has contributed to a stronger Euro against the Dollar over the last several weeks.
Here are some key events to watch in relation to the EUR/USD:
Friday, January 5, 2024, EA Inflation Rate YoY Flash DEC & Core Inflation Rate YoY Flash DEC: These releases provide the latest inflation figures for the Euro-Area. Higher-than-expected inflation may strengthen the Euro as it could pressure the ECB to maintain or even increase rates, while lower figures might suggest the opposite, potentially weakening the Euro against the Dollar.
Monday, January 8, 2024, EA Economic Sentiment DEC & Retail Sales MoM NOV: These indicators give insight into consumer confidence and retail activity within the Euro-Area. Positive data could bolster the Euro by indicating a resilient economy, while negative data could hint at economic slowdown, potentially weakening the Euro.
Tuesday, January 9, 2024, EA Unemployment Rate NOV: This is a critical indicator of economic health. Lower unemployment rates might strengthen the Euro as they suggest a stronger economy, whereas higher rates could indicate economic troubles, potentially weakening the Euro.
Wednesday, January 3, 2024, US FOMC Minutes & ISM Manufacturing PMI DEC: The FOMC minutes will provide insights into the Federal Reserve's monetary policy outlook, which is crucial for the Dollar. A dovish tilt could weaken the Dollar, strengthening the EUR/USD. The ISM Manufacturing PMI serves as a barometer for U.S. economic health; lower figures might weaken the Dollar, while higher figures could strengthen it.
Friday, January 5, 2024, US Non-Farm Payrolls & Unemployment Rate DEC: These are significant indicators of U.S. economic health. Strong job growth and a lower unemployment rate could signal a robust economy and strengthen the Dollar, potentially lowering the EUR/USD, whereas weaker figures might have the opposite effect.
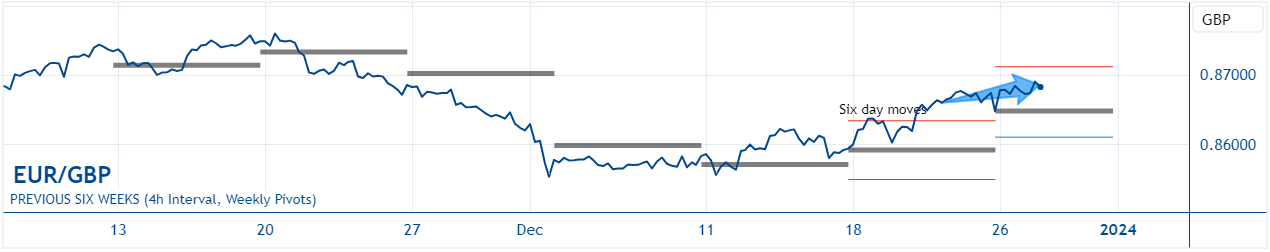
EUR/GBP: Over the short term, the EUR/GBP has gained a little value since December 21, reflecting the interplay of monetary policy expectations and economic outlooks in the Euro-Area and the UK. The Euro has found short-term strength amid expectations that the Federal Reserve will commence rate cuts earlier and more aggressively than the European Central Bank. This perception, coupled with a relatively hawkish ECB compared to other major central banks, has temporarily bolstered the Euro against a backdrop of general dollar weakness. Conversely, the Pound has been somewhat pressured by the dual narrative of anticipated Bank of England rate cuts amid softening inflation and economic slowdown, despite high current interest rates. Over the long term, since November 15, the EUR/GBP has lost some value. This reflects a more pronounced concern over the Euro-Area's economic challenges, including high inflation and a slight GDP contraction, which have prompted the ECB to maintain a restrictive stance, potentially dampening growth prospects. Meanwhile, the Pound, despite facing similar pressures, has been somewhat buoyed by the Bank of England's relatively more cautious approach to rate cuts and the UK's tight labour market, suggesting a stronger short-term economic resilience compared to the Euro-Area. The contrast between the ECB's aggressive stance on inflation and the Bank of England's cautious rate outlook amidst economic headwinds has influenced the longer-term trajectory of the EUR/GBP exchange rate.
Here are some key events to watch in relation to the EUR/GBP:
Friday, January 5, 2024, EA Inflation Rate YoY Flash DEC: This data will give insights into the Euro-Area's inflation trends, which are critical for the ECB's monetary policy decisions. Higher than expected inflation may support a stronger Euro if it suggests continued hawkishness from the ECB.
Friday, January 5, 2024, EA Core Inflation Rate YoY Flash DEC: Core inflation is a key indicator the ECB uses to assess the underlying inflationary pressures. A higher or sustained core inflation rate could bolster the Euro by indicating that the ECB might maintain or delay its rate cuts.
Friday, January 5, 2024, GB Halifax House Price Index YoY DEC: This indicator provides insight into the UK's housing market, a significant component of the economy. A weaker housing market might suggest broader economic challenges, potentially weakening the Pound.
Tuesday, January 9, 2024, EA Unemployment Rate NOV: The unemployment rate is a critical indicator of economic health. A significant decrease or an unexpected increase could influence the Euro by altering perceptions of the Euro-Area's economic recovery and, thus, the ECB's policy stance.
Friday, January 12, 2024, GB GDP MoM NOV: GDP growth is a primary indicator of economic health. A higher than expected growth rate could strengthen the Pound by suggesting resilience in the UK economy, possibly influencing the Bank of England's monetary policy outlook. Conversely, a contraction could pressure the Pound if it implies prolonged economic weakness.
Gavin Pearson
Retail trader since 2008
Specialises in forex G7 currencies
Funded account from the 5ers.com
Member of the eToro Popular Investors Program
Regular contributor to FXStreet.com analysis and education pages
Returned 27% in 2022 and 5.8% in 2023 H1
Forex focused
Copy Trading available at eToro
Disclaimer
Past performance is not indicative of future results
Trading involves risk, and you could lose money
-end-