USD Fundamental Analysis: June 12th FOMC Meeting Pivotal to Next Direction
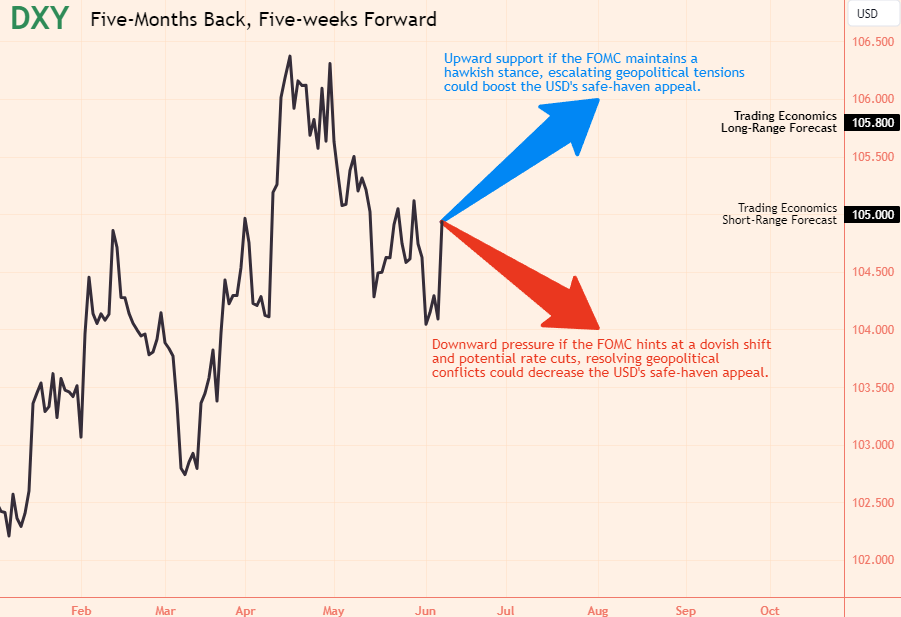
Saturday, 8 June 2024, Week 23: The USD has been on a rollercoaster ride over recent months. After a five-month period of robust strength, the currency has shown signs of indifference over the past five weeks. This shift in sentiment is largely attributed to the Federal Reserve's decision to pause its rate hiking cycle and the uncertainty surrounding the future path of monetary policy. With the FOMC meeting scheduled for June 12th, the market is poised for a potential turning point. This report provides a comprehensive analysis of the key factors influencing the USD, examining fiscal policy, economic indicators, monetary policy, and geopolitical events to provide insights into the currency's potential trajectory.
Fiscal Policy
The US government's fiscal policy stance is currently characterised by a focus on deficit reduction, as outlined in the 2025 Federal Budget. The budget proposes ambitious plans to reduce the deficit by $3 trillion over the next decade, primarily through measures such as increased taxes for high-income earners and corporations, closing tax loopholes, and reducing spending on subsidies. These fiscal tightening measures are intended to offset the expansionary impact of proposed investments in key areas like childcare, education, healthcare, infrastructure, and climate change.
Looking ahead to the next five weeks, the spotlight will likely shift towards the upcoming Farm Bill reauthorization. The Administration has outlined its priorities for the Farm Bill, including support for new and beginning farmers, bolstering agricultural research, addressing climate change through conservation and clean energy investments, and promoting competition in agricultural markets. The outcome of the Farm Bill negotiations could have significant implications for agricultural commodity prices, rural economic development, and overall fiscal spending. The market will be closely watching for any developments that could signal a shift in the government's fiscal stance.
Economics
The US economy is currently navigating a period of solid, albeit moderating, growth. The labour market remains tight, characterised by strong job gains and a low unemployment rate. However, persistent inflation continues to pose a challenge for the Federal Reserve as it strives to achieve its 2 percent inflation target.
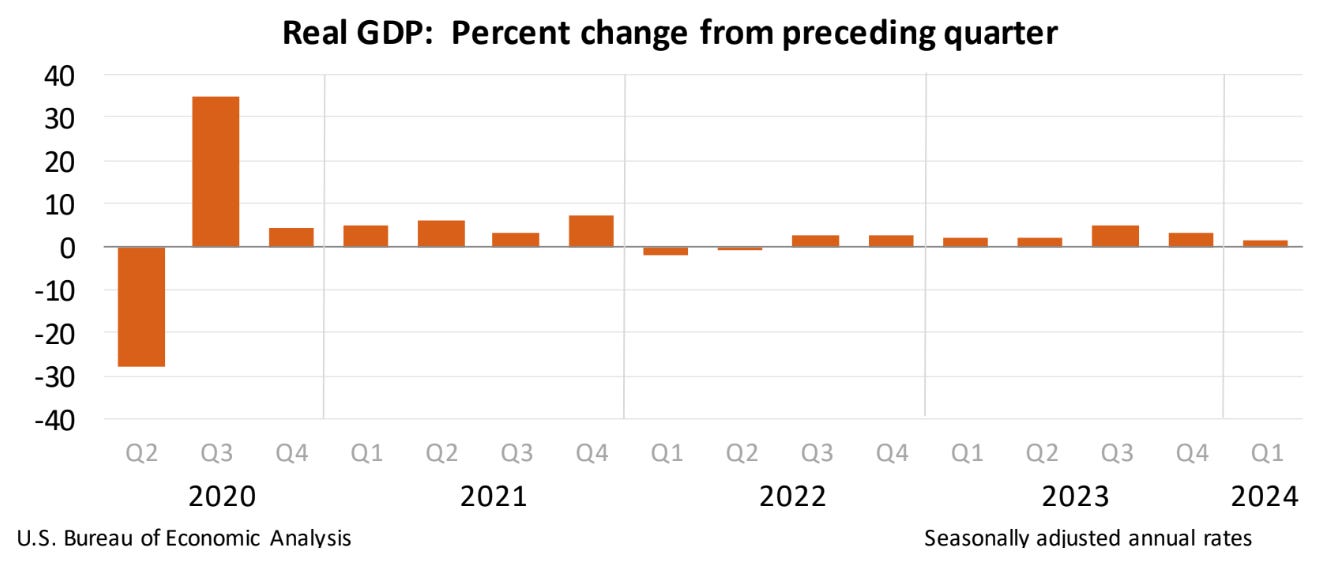
Economic Growth: The second estimate for Q1 2024 GDP growth, released on May 30th, revealed an annualised expansion of 1.3 percent. This figure fell short of the advance estimate of 1.6 percent and marked a significant slowdown from the 3.4 percent growth recorded in Q4 2023. The downward revision was primarily attributed to a larger-than-anticipated slowdown in consumer spending. The U.S. Bureau of Economic Analysis stated, "The increase in real GDP primarily reflected increases in consumer spending, residential fixed investment, nonresidential fixed investment, and state and local government spending that were partly offset by a decrease in private inventory investment."
Over the next five weeks, the release of the third estimate of Q1 GDP growth, scheduled for June 27th, will be a key event for assessing the economy's momentum. Additionally, incoming data on retail sales, industrial production, and consumer confidence will provide further insights into the strength of economic activity.
Labour: The US labour market continues to exhibit resilience, with nonfarm payrolls surging by 272,000 in May, exceeding market expectations and marking the most substantial increase in five months. However, the unemployment rate unexpectedly rose to 4.0 percent, reaching its highest level since January 2022. This uptick in unemployment, coupled with a decline in the labour force participation rate, suggests that the labour market may be starting to loosen. Despite this, average hourly earnings for all employees on private nonfarm payrolls rose by 0.4 percent in May, indicating that wage pressures remain a concern. Nela Richardson, chief economist at ADP, commented, "Job gains and pay growth are slowing going into the second half of the year. The labour market is solid, but we're monitoring notable pockets of weakness tied to both producers and consumers."
Looking ahead to the next five weeks, the release of the June employment report, scheduled for July 5th, will be a crucial data point for gauging the labour market's health. Additionally, data on job openings, initial jobless claims, and the employment cost index will provide further insights into labour market dynamics.
Price Changes: Inflation remains a key concern for the Federal Reserve, with the annual inflation rate easing to 3.4 percent in April, but still exceeding the Fed's 2 percent target. Core inflation, which excludes volatile food and energy prices, slowed to a three-year low of 3.6 percent in April. However, the recent uptick in consumer inflation expectations, as measured by the Federal Reserve Bank of New York, suggests that consumers anticipate persistent inflationary pressures.
The release of the May CPI report, scheduled for June 12th, will be a pivotal event for assessing the trajectory of inflation over the next five weeks. Additionally, data on producer prices and personal consumption expenditures will provide further insights into price pressures.
Trade: The US trade deficit widened to $74.6 billion in April, reaching its highest level since October 2022. This expansion in the trade gap was driven by a 2.4 percent increase in imports, outpacing a meagre 0.8 percent increase in exports. The widening trade deficit suggests that net exports could continue to weigh on economic growth in the second quarter.
The release of the May trade report, scheduled for July 3rd, will be an important data point for assessing the trade balance's impact on the economy over the next five weeks.
Monetary Policy
The Federal Reserve has adopted a hawkish stance, maintaining the target range for the federal funds rate at 5.25-5.50 percent for the sixth consecutive time in its May meeting. Despite this, the Fed has signalled its intention to slow the pace of its quantitative tightening program, reducing the monthly redemption cap on Treasury securities from $60 billion to $25 billion starting in June. The FOMC statement acknowledged the recent slowdown in economic growth while reiterating its commitment to fighting inflation: "The Committee judges that the risks to achieving its employment and inflation goals have moved toward better balance over the past year. The economic outlook is uncertain, and the Committee remains highly attentive to inflation risks."
The FOMC meeting scheduled for June 12th will be a pivotal event for assessing the Fed's policy path over the next five weeks. Market participants will be closely scrutinising the accompanying statement, economic projections, and Chair Powell's press conference for clues about the timing and extent of potential rate cuts.
Geopolitics and Market Themes
Several geopolitical situations and market themes are currently influencing financial markets, including:
Russia-Ukraine War
The ongoing war in Ukraine continues to cast a shadow over global risk sentiment, contributing to market volatility and uncertainty.
Russia is expected to make tactical gains in Ukraine in the coming months, capitalising on Kyiv's manpower and equipment shortages.
Western support for Ukraine remains strong, but there are growing concerns about the long-term sustainability of aid.
The war has disrupted global supply chains, particularly for energy and agricultural products, contributing to inflationary pressures.
The war has increased demand for safe-haven assets, such as the USD and gold.
European currencies, particularly the EUR, have weakened against the USD due to the war's impact on the European economy.
Energy prices remain elevated, with the potential for further volatility depending on the war's trajectory.
Israel-Hamas War
The recent escalation of violence between Israel and Hamas has added to geopolitical uncertainty, impacting risk appetite and market sentiment.
Israel has reoccupied Gaza and is expected to shift its focus to Hezbollah in Lebanon, raising the risk of a wider conflict.
Western and Arab states are calling for a ceasefire, but a diplomatic solution remains elusive.
The conflict has heightened tensions in the Middle East, with the potential for spillover effects in the region.
The conflict has contributed to risk aversion, boosting demand for safe-haven assets.
Oil prices have risen due to concerns about potential supply disruptions in the Middle East.
The Israeli Shekel has weakened against the USD amid heightened uncertainty.
Global Interest Rate Hikes
Central banks worldwide are raising interest rates to combat persistent inflation, impacting economic growth and market sentiment.
The US Federal Reserve has paused its rate hiking cycle, but is expected to keep rates elevated for an extended period.
The European Central Bank recently cut interest rates, but signalled that further cuts are contingent on inflation slowing as expected.
The Bank of England is expected to cut rates later in the year, but remains concerned about inflation.
Rising interest rates are increasing borrowing costs for businesses and consumers, weighing on economic growth.
Higher interest rates are supporting the USD, as investors seek higher yields.
Currencies in countries with lower interest rates, such as the EUR and JPY, have weakened against the USD.
Rising interest rates are weighing on stock markets, as investors anticipate slower economic growth.
Persistent Inflation
Inflation remains elevated in many countries, eroding consumer purchasing power and prompting central banks to maintain tight monetary policies.
Inflation in the United States has moderated, but remains above the Federal Reserve's 2% target.
Inflation in the Eurozone has rebounded, raising concerns about the ECB's ability to bring inflation under control.
Inflation in the United Kingdom has eased, but remains above the Bank of England's 2% target.
Persistent inflation is pressuring businesses to raise prices, further contributing to inflationary pressures.
Inflation is supporting demand for inflation-hedging assets, such as gold.
Currencies in countries with higher inflation, such as the GBP, have weakened against the USD.
Persistent inflation is creating uncertainty for businesses and consumers, weighing on economic growth and market sentiment.
Mexico Landslide Election Result
The Morena party's supermajority victory in Mexico's June 2 election has raised concerns about potential constitutional reforms that could impact investor confidence.
The Morena party, led by President Andrés Manuel López Obrador, secured a supermajority in both houses of Congress.
The victory could empower the Morena party to implement significant constitutional reforms, including changes to the energy sector and the judiciary.
Investors are concerned that these reforms could undermine investor confidence and negatively impact the Mexican economy.
The Mexican Peso has weakened sharply against the USD in response to these concerns.
Mexican stocks have also declined, reflecting investor uncertainty about the economic outlook.
"The outcome consolidates AMLO’s political hold and will make it more difficult for Sheinbaum to diverge from his road map,"" said Felipe Hernandez, a Latin America economist at Bloomberg Economics.
Conclusion
The USD's performance over the next five weeks will be heavily influenced by the outcome of the FOMC meeting on June 12th. The following scenarios outline potential paths for the USD:
Upward Support: The USD could resume its strengthening trend if the FOMC maintains its hawkish stance, signalling that interest rates will remain elevated for an extended period. A higher-than-expected CPI reading on June 12th would reinforce this outlook, as it would suggest that inflation is more persistent than anticipated. Additionally, escalating geopolitical tensions, particularly in the Middle East, could further boost demand for the USD as a safe-haven asset.
Indifference: The USD could continue to trade sideways if the FOMC strikes a more balanced tone, acknowledging the recent slowdown in economic growth while reiterating its commitment to fighting inflation. A mixed CPI report, with some signs of easing price pressures, could support this scenario. Additionally, a de-escalation of geopolitical tensions could reduce safe-haven demand for the USD.
Downside Pressure: The USD could weaken if the FOMC signals a potential shift towards a more dovish stance, hinting at the possibility of rate cuts later in the year. A lower-than-expected CPI reading on June 12th would increase the likelihood of this scenario, as it would suggest that inflation is moderating more quickly than anticipated. Additionally, a resolution of geopolitical conflicts could further weigh on the USD by reducing safe-haven demand.
References
Federal Reserve: https://www.federalreserve.gov/
U.S. Bureau of Economic Analysis: https://www.bea.gov/
Automatic Data Processing, Inc.: https://www.adp.com/
U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics: https://www.bls.gov/
Institute for Supply Management: https://www.ismworld.org/
National Federation of Independent Business: https://www.nfib.com/
University of Michigan: https://data.sca.isr.umich.edu/
Technometrica Market Intelligence: https://www.realclearmarkets.com/
Bloomberg: https://www.bloomberg.com/
Trading Economics: https://tradingeconomics.com/
Office of Management and Budget, The White House: https://www.whitehouse.gov/omb/
2025 US Federal Budget
Consumer Price Index - April 2024
The Employment Situation - May 2024
Minutes of the Federal Open Market Committee April 30–May 1, 2024
Transcript of Chair Powell’s Press Conference May 1, 2024
Gross Domestic Product (Second Estimate), Corporate Profits (Preliminary Estimate), First Quarter 2024
U.S. International Trade in Goods and Services, April 2024
U.S. International Transactions, 4th Quarter and Year 2023